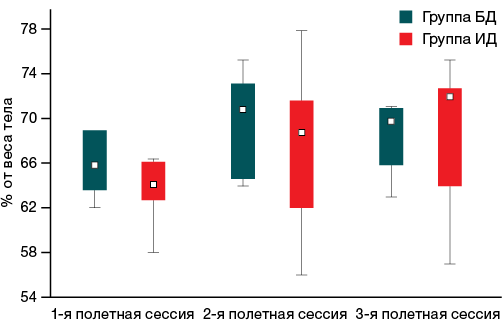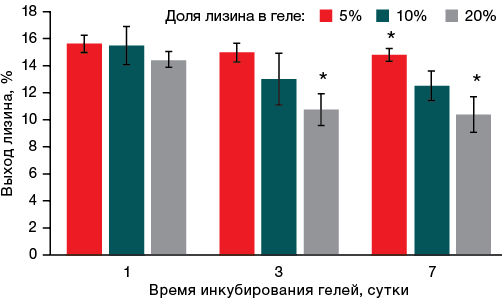MAIN TOPIC: TOPICAL ISSUES OF CLINICAL NEUROLOGY & NEUROLOGICAL DISORDER INSTRUMENTAL DIAGNOSTICS
Introduction. Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) are gradually progressive neurodegenerative diseases leading to disability. According to literature data, POAG can be a predictor of AD development. Early diagnosis of these diseases contributes to a timely initiation of treatment and, as a result, a reduction in the disability of patients.
Objective. To study biomarkers of early diagnosis in biological fluids and neuroimaging changes based on the results of MR morphometry in patients with AD and POAG and to conduct their comparative analysis.
Materials and methods. In total, 90 patients with proven diagnosis of AD (group 1) and POAG (group 2) were examined. The study participants were divided into two groups according to their diagnosis: group 1 — 45 patients (9 (20%) men and 36 (80%) women) with AD; group 2 — 45 people (17 (37.8%) men and 28 (62.2%) women) with POAG. Neuropsychological testing included Mini-mental State Examination (MMSE), Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), and a ten-words recall test. The beta-amyloid (Aβ) Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio in the blood and sirtuin Sirt1, 3, 5, and 6 in saliva were assessed by enzyme immunoassay (ELISA). In addition, MR morphometry of the brain was performed.
Results. In group 1, cognitive impairments (CI) reaching the degree of dementia were detected; in group 2, pre-demential CI were observed (p < 0.001). According to the neuropsychological examination, similar changes were noted in both groups, in particular, memory impairment of the hippocampal type. The results of the blood and saliva ELISA with the determination of biomarkers in the groups under comparison did not reveal statistically significant differences. At the same time, the parameters of both volumes and thicknesses according to MR morphometry were lower in group 1 (p < 0.05), which may reflect neurodegenerative progression. In group 1, a direct correlation was found between a decrease in the saliva level of Sirt3 and a deterioration in direct reproduction (fifth reproduction) according to the ten-words recall test (R = 0.43; p = 0.003). Correlations between changes in neuropsychological parameters and MR morphometry data, including a decrease in the volume of the entorhinal cortex, were noted in both groups. In groups 1 and 2, a decrease in the Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio in blood plasma was associated with a decrease in the thickness or volume of the entorhinal cortex, which is common for both groups with different CI severity. Taking into account the association with neuropsychological and blood parameters, including in patients with pre-demential CI from the POAG group, the determination of the volume and thickness of the entorhinal cortex can be regarded as a significant early marker of the neurodegenerative process.
Conclusions. The established association between the volume and thickness of the entorhinal cortex with neuropsychological and blood parameters, including in patients with pre-demential CI from the POAG group, makes the determination of the volume and thickness of the entorhinal cortex a significant early marker of the neurodegenerative process. A comprehensive assessment of the results obtained by neuropsychological, laboratory, and neuroimaging diagnostic methods, as well as the search for diseases associated with the development of AD, such as POAG, are promising research areas, requiring larger cohort studies.
Introduction. The range of pathologies and conditions that can lead to the development of rapidly progressive dementia (RPD) is rather extensive. Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is considered the most common cause of dementia. However, there are other pathologies that, unlike AD, are curable, and, given accurate diagnosis, allow a complete regression of pathological symptoms to be achieved. This highlights the importance of differential diagnosis of rapidly progressing AD from other causes of RPD.
Objective. To determine the differential features of rapidly progressing AD and to study the main causes predisposing to the development of RPD but not related to neurodegenerative pathology.
Discussion. Rapidly progressing AD differs from typical AD in the rate of cognitive decline. On average, rapidly progressing AD is associated with a loss of three points or more scores on the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) test within six months and a faster (in 2–3 years) achievement of the terminal stage of the disease. In case of typical AD, this period is longer, lasting for about 8–10 years. Other major causes of RPD include prion diseases, neurodegenerative diseases of non-prion etiology (including rapidly progressing AD), vascular diseases, infectious diseases, inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, oncological diseases, metabolic and deficiency disorders, endocrine disorders, toxic and iatrogenic disorders, mental diseases, and cerebrovascular pathology.
Conclusions. Identification of the RPD cause requires a detailed and comprehensive examination of the patient using various laboratory and instrumental research methods, which is the key to accurate diagnosis and further successful drug correction of terminal diseases. Positron emission tomography of the brain and such biomarkers as beta-amyloid and hyperphosphorylated tau protein in the cerebrospinal fluid play a major role in the diagnosis of rapidly progressive AD and differential diagnosis from other RPD causes.
Introduction. About 30–40% of patients who have suffered from acute cerebrovascular accident (ACVA) experience a syndrome of unilateral spatial neglect. Neuropsychological testing (NT) is a routine diagnostic technique, while the method eye tracking offers prospects for an objective assessment of visual attention.
Objective. Evaluation of the diagnostic capabilities of classical neuropsychological techniques and eye tracking to detect the neglect syndrome in stroke patients.
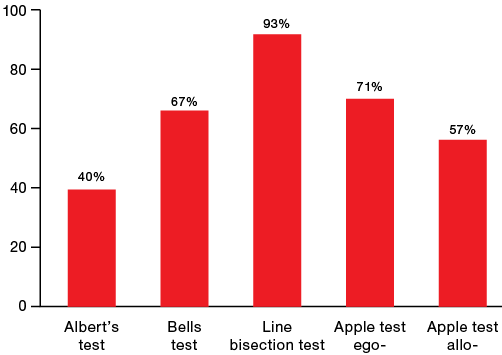
Materials and methods. The study involved 38 stroke patients (25 men, 13 women; mean age 59.7 ± 12.7 years). The Bells test (BT), Albert’s test (AT), Line bisection test (LBS), the computer version of the Apple test (ApT), and the eye tracking method (a search task for recording visual activity) were used to diagnose the neglect syndrome.
Results. The LBS test data demonstrated the greatest sensitivity in the detection of neglect syndrome. Significant correlations (p < 0.01) were obtained between the results of BT, AT, LBS, and ApT and the results of eye tracker visual search (p = 0.025), indicating the detection of a similar degree of observed deficiency by different methods. The latency of finding stimuli in the left half-field when performing a search task on an eye tracker is significantly higher than in the right side (p < 0.001). Ischemic stroke patients performed AT worse (p = 0.009) than hemorrhagic stroke patients, and they were more mistaken in LBS (p = 0.043). The more pronounced severity of the patients’ neglect, the worse the AT (p = 0.004), LBS (p = 0.05), and Aptego (p = 0.036) were performed. The visual impairment factor had a significant effect in LBS testing (p = 0.02).
Conclusions. The combination of neuropsychological tests and eye tracking provides objective data for the diagnosis of neglect syndrome. The LBS test demonstrated the greatest sensitivity in detecting the neglect syndrome. The results of eye tracking were found to be comparable with those of pencil-and-paper tests, which increases the accuracy of the diagnosis of neglect syndrome. The following factors influencing the performance of diagnostic tests were identified: stroke type, neglect severity, and visual impairment.
Introduction. Post-stroke cognitive impairment (PSCI) is an important medical and social problem, with its prevalence reaching the level of 74%.
Objective. To study the relationship between integral parameters characterizing the processes of coagulation and fibrinolysis, determined using dynamic thrombophotometry, and PSCI formation with the purpose of assessing the possibility of predicting PSCI and adverse disease outcomes.
Materials and methods. The study included 35 patients who had suffered an ischemic stroke within 24 hours of the onset of the disease: 20 (57.1%) women and 15 (42.9%) men; the median age was 66.5 [62.3–73.3] years. The comparison group included 45 conditionally healthy volunteers. Assessment of the state of the hemostasis system was carried out upon admission to the hospital, on days 6–8 and 13–15. Integral indicators evaluating the coagulation, fibrinolysis, and hemostasis systems in general were studied using the Fibrinodynamics method. Cognitive functions were assessed on days 10–14 according to the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) scale. The functional outcome of the disease was determined by the Modified Rankin Scale (mRS) on day 28. The SPSS 27.0 software (IBM, USA) was used for statistical analysis. Associations between continuous data were evaluated using the Spearman correlation coefficient, one-dimensional and multidimensional linear regression models. The difference at the level of p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results. An inverse correlation was found between the average brightness of the clot during the integral modeling of hemostasis processes at admission and the level of cognitive dysfunction on the MoCA scale (rs = –0.409; p = 0.02); higher initial HB values were associated with severe post-stroke cognitive impairment. Conversely, a direct relationship between the initial fibrinolysis of the resulting clot (FB) and cognitive impairment on the MoCA scale (r = 0.512, p = 0.003) was found; higher values of FB corresponded to a higher score on the MoCA scale and a higher level of cognitive functions.
Conclusions. Predictive multidimensional linear regression models that included age and baseline stroke severity found that an increase in baseline HB by every 11.5 arbitrary units or a decrease in baseline FB by 9.8 arbitrary units corresponded to a minus 1 point deterioration in the cognitive status when assessed by MoCA. Patients with higher baseline values of FB had more favorable functional outcomes of the disease according to (mRS). The use of dynamic thrombophotometry and its extended version makes it possible to comprehensively assess changes in the hemostasis system of patients with ischemic stroke. Higher HB values and lower FB values make it possible to predict an unfavorable outcome of the disease and more severe PSCI in the early stages, while the hypoactivation of the fibrinolytic system is associated with a greater severity of PSCI and a less favorable functional outcome.
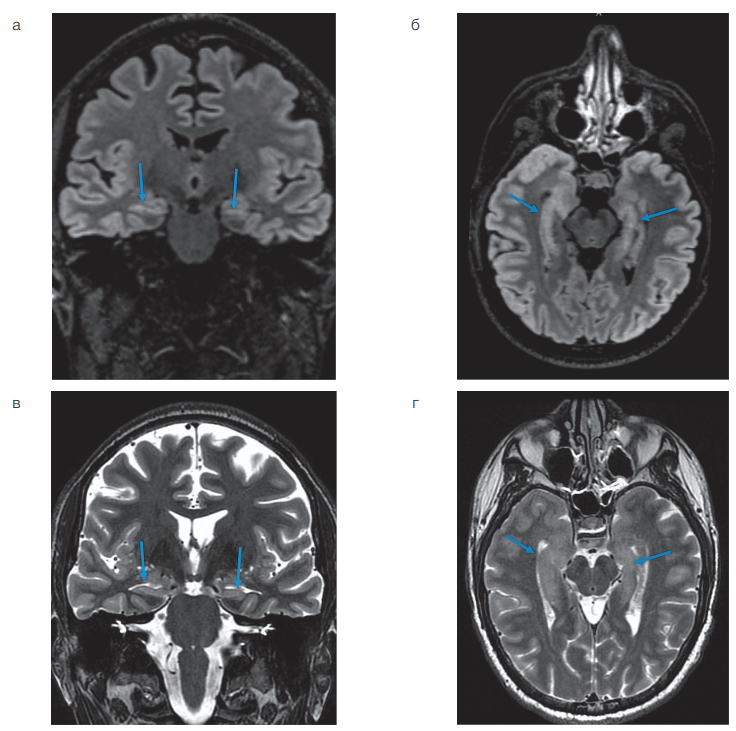
Introduction. Localization of an epileptic focus (EF) in patients with pharmacoresistant focal epilepsy can be a challenging task, and the detection of multiple EFs limits the possibilities of surgical treatment. A more accurate description of the structure and metabolism of EFs may provide additional information for managing such patients.
Clinical case description. A 35-year-old patient suffered from pharmacoresistant focal epilepsy, which debuted at the age of 24 with grand mal seizures followed by focal episodes with fading and tonic tension of the left arm. The MRI revealed bilateral mesial temporal sclerosis with more pronounced changes on the left; however, the EEG revealed epileptiform activity in the right temporal region, which created diagnostic difficulties in determining the primary epileptogenic zone. To clarify the location of the lesion, a comprehensive examination was performed, including PET/MRI, which revealed pronounced hypometabolism in the right temporal lobe (with a difference of up to 31% compared with the contralateral side) while maintaining symmetrical accumulation of RPh in the hippocampus. Additionally, diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) was performed, which showed a significant decrease in radial and median kurtosis, as well as axonal water fraction in the right temporal lobe (up to 1.33 SD from normal). Invasive EEG monitoring confirmed the bilateral nature of epileptogenicity with a predominance of right-hemisphere seizure initiation.
Conclusions. The combined use of PET/MRI and DKI increases the accuracy of detection of epileptogenic foci in pharmacoresistant epilepsy. Hybrid imaging allows for a comprehensive assessment of metabolic and microstructural changes, which is important for planning surgical treatment. Data integration helps differentiate primary and secondary foci, thus optimizing patient management tactics. The introduction of automated analysis for standardization of diagnostics is promising.
Introduction. Being the most common tumor of the central nervous system with an extremely unfavorable prognosis, glioblastoma remain to be a major health issue. Conventional neuro-oncological strategies demonstrate insufficient effectiveness, which requires the development of improved approaches.
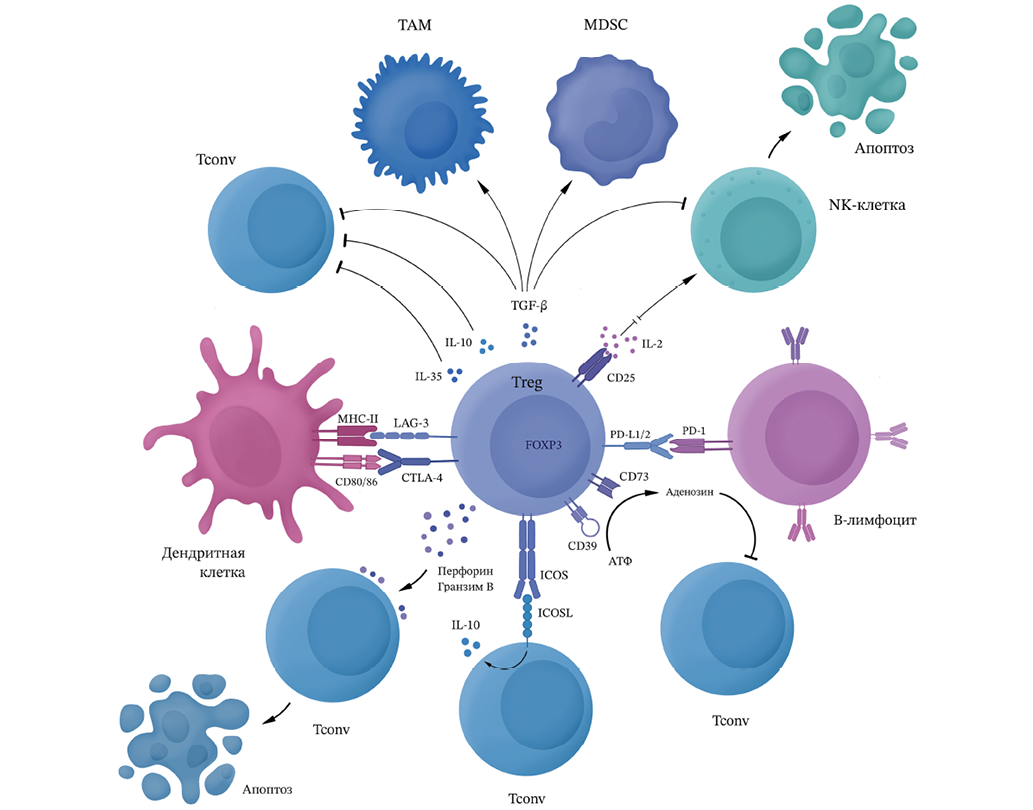
Objective. Analysis of the mechanisms of functioning of regulatory T lymphocytes (Treg) in the tumor microenvironment as a potential target for therapy, as well as identification of promising therapeutic methods to reduce the suppressive effect of regulatory T lymphocytes in glioblastoma.
Discussion. The resistance of glioblastoma against antitumor immunity and the low effectiveness of some types of treatment is largely related to the immunosuppressive microenvironment of the tumor, the key components of which are Treg. Tregs suppress the antitumor response through the secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines, perforins, and granzymes, as well as the expression of inhibitory molecules. Drugs that selectively affect the metabolic pathways of activation, differentiation, and migration of regulatory T cells can reduce their activity and total number in the microenvironment.
Conclusions. Tregs can act as a target for therapy aimed at suppressing the immunosuppressive microenvironment of the tumor, reducing the activity and progression of glioblastoma. New targeted therapeutical approaches may supplement the existing standards of glioblastoma treatment.
SPACE MEDICINE
Introduction. The improvement of methods for remote health monitoring of astronauts, as well as the search for new noninvasive biomarkers of metabolic adaptation to microgravity conditions, are priority directions in the field of aerospace medicine.
Objective. To assess the possibility of using individual indicators of tear fluid in aerospace medicine.
Discussion. A number of prospects for the application of human tear biomarkers to determine disorders occurring under the influence of spaceflight factors or during their imitation were identified. The use of filter paper is a priority method for collecting lachrymal fluid in spaceflight conditions due to its relative noninvasiveness and simplicity of sample preparation for assay. It was found that the unstimulated tear fluid contains proteins with an antibacterial activity: lysozyme, lipocalin, and secretory immunoglobulin A. The concentration of lysozyme in the tear fluid shows a marked increase relative to pre- and post-flight values. Changes in the concentration of natriuretic peptide, angiotensin II, dopamine, and α2-macroglobulin under conditions of real and simulated microgravity are described. A high diagnostic potential of determining the level of D-dimer in tear fluid under the influence of extreme factors of space flight was established.
Conclusions. The conducted literature review emphasizes the significant theoretical potential for the quantitative determination of natriuretic peptide, D-dimer, and individual components of the dopamine and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone systems in tear fluid for noninvasive diagnostics of pathological processes associated with spaceflight factors.
Introduction. In Russia, locomotor training is the key approach to mitigating the negative effects of weightlessness. Locomotor training is performed according to strictly defined protocols, without individualization and periodization of the training process.
Objective. To study the effect of periodization of locomotor training on the performance of crewmembers during long-term space missions.
Materials and methods. The study involved 12 cosmonauts, who were divided into two groups. The first group (BD, n = 6) included the participants who performed locomotor training in strict accordance with the standard on-board documentation system. The second group (ID, n = 6) included the participants who performed training using individual protocols and periodization of the training process. The assessment of physical performance was carried out according to the results of a regular stepwise locomotive test prior to a spaceflight (SF) mission and three times during SF. The test evaluated the achieved speeds at the most intensive stages of testing, the distance traveled during the test, and heart beats per distance (pulse value performance). Statistical processing was carried out in Statistica 10; nonparametric methods of descriptive statistics were used.
Results. In the second part of SF, cosmonauts in the ID group reached higher speeds at the stages of medium and fast running and covered a greater distance by 18.5–20.7% (p < 0.05) and 5–12% (p < 0.05) compared with the BD group and with the baseline testing, respectively. The beats per distance in the ID group was lower throughout the SF compared to both the baseline values and the BD group in the 2nd and 3rd flight testing sessions.
Conclusions. In the conditions of SF, locomotor training programs based on periodization and individualization demonstrate a greater preventive effectiveness compared to standard on-board training.
Introduction. Dry immersion is a model for reproducing the physiological effects of weightlessness. Such tests allow assessment of changes in the functions of the cardiovascular, musculoskeletal, and other body systems. Mass spectrometry instruments can be used for blood proteome analysis in order to establish mechanisms of physiological adaptation to spaceflight factors simulated in dry immersion tests.
Objective. To clarify molecular participants in the acute period of adaptation of physiological systems to the conditions of simulated microgravity according to proteome analysis of dry blood spots of participants in a five-day dry immersion test.
Materials and methods. The study involved eight healthy female volunteers (average age 30 ± 4.8 years). Blood proteins were analyzed using the method of dried blood spots; capillary blood dried on a special paper filter (Perkin Elmer) was used. The enzyme cleavage of proteins was performed using trypsin (Thermo Scientific, USA). Mixtures of tryptic peptides were analyzed by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC–MS) on a Dionex Ultimate 3000 nano-HPLC combined with a TimsTOF Pro mass spectrometer. Mass spectrometric analysis was performed using the method of parallel accumulation with
sequential fragmentation (PASEF). The obtained LC–MS/MS data were semi-quantitatively analyzed using DIA-NN 1.8.1. Statistical analysis was performed in the Statistica 12 software package.
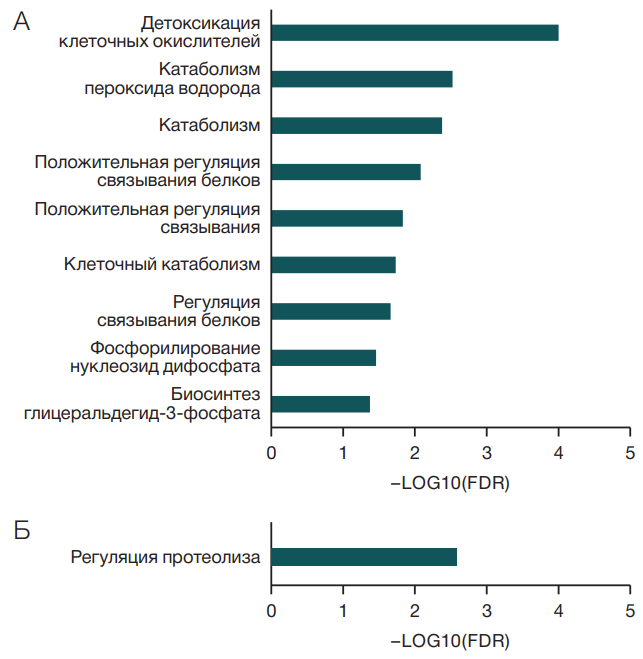
Results. The molecular response to immersion conditions was found to lead to increased levels of antioxidant defense proteins, activation of catabolism processes and the pentose phosphate pathway. The levels of negative regulators of endopeptidases and iron homeostasis proteins decreased. The revealed elevated levels of NADPH oxidase activators indicate activation of NADPH oxidase under experimental conditions. These results may indicate the development of oxidative stress during immersion.
Conclusions. The identified molecular participants in the female body’s response to immersion conditions can provide information about the signaling pathways and mechanisms involved in the response to hypokinesia, and in the future will contribute to the development of pharmacological measures to support the health of female astronauts. These results may also be useful for understanding the processes leading to adverse effects in people with low levels of physical activity.
PULMONOLOGY
Introduction. Genetically engineered biological drugs (GEBD) are widely used in the treatment of children with uncontrolled bronchial asthma (BA). In Russia, several GEBD have been registered for the treatment of children and adolescents with asthma, including anti-immunoglobulin E/anti-IgE (omalizumab), anti-interleukin 5/anti-IL-5Ra (mepolizumab), and anti-IL-4Ra (dupilumab). The choice of GEBD depends on the BA phenotype and genotype. However, in pediatric practice, the difficulty of determining a BA endotype complicates the search for an effective drug. For this reason, there is a possibility of insufficient effectiveness of the recommended expensive therapy and the need to revise the treatment of GEBD in accordance with the phenotypic features of the disease.
Clinical case description. The paper presents a dynamic follow-up of a 7-year-old child with severe asthma and concomitant atopic dermatitis (AD) receiving GEBD therapy. The initial biological drug was omalizumab. Subsequently, due to insufficient control of the symptoms of the disease and exacerbation of severe atopic dermatitis, a switch to dupilumab was performed. The change in GEBD contributed to achieving control over BA symptoms and a relief of the skin condition.
Conclusions. Our observation shows the effectiveness and safety of switching between omalizumab to dupilumab in children with severe asthma and concomitant AD. Further research is needed to clarify the clinical profile of patients in order to determine predictors of an effective choice of biotherapy and resolve the issue of switching to various monoclonal antibodies.
RADIOBIOLOGY
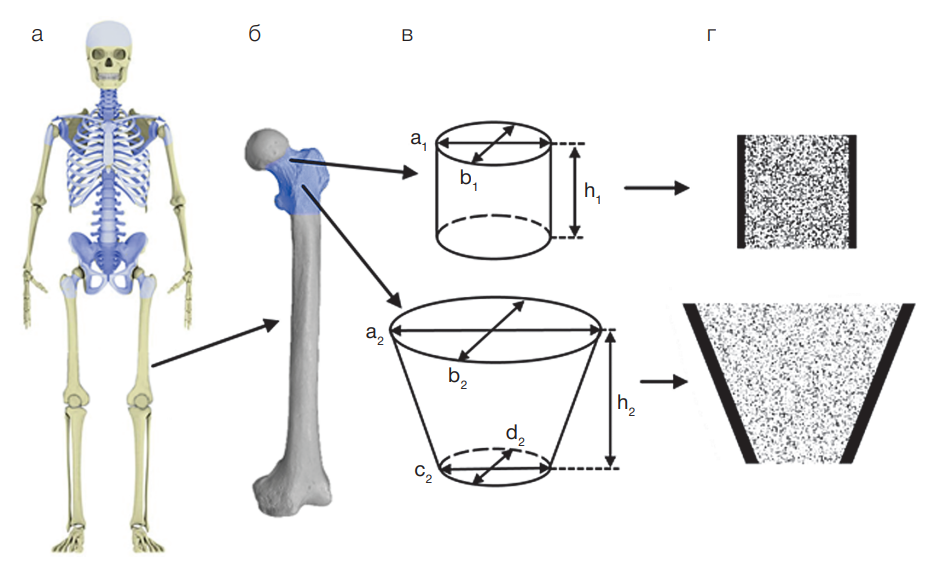
Introduction. The dose assessment of internal irradiation of red bone marrow (RBM) by osteotropic radionuclides is based on dosimetric modeling using computational phantoms. Creating such phantoms for 89.90Sr requires careful description of the shape and size of bones, as well as their microarchitecture. Descriptions of phantoms representing newborn, one-year-old, 5-year-old, and 10-year-old children have been published. Our study continues work on creating a set of computational skeletal phantoms for people of different ages.
Objective. Development of computational skeletal phantoms of male and female adults for estimating radiation doses of beta-emitting radionuclides incorporated in RBM.
Materials and methods. The stochastic parametric skeletal dosimetry (SPSD) method of creating phantoms was used. The skeletal sections with active hematopoiesis were divided into segments. On the basis of literature data, the parameters of segment models were evaluated: linear dimensions, cortical layer thickness, bone microarchitecture characteristics, density, chemical composition, and RBM proportion.
Results. The developed phantoms of male and female adults are composite, including 46 segments each; the parameters of 21 segments were independent of sex. The sizes of segment phantoms range within 4–66 mm; the cortical layer thickness ranges within 0.3–2.2 mm. The parameters of bone segment microarchitecture are presented.
Conclusions. The resulting phantoms simulate the microand macro-architecture of bone tissue, and, together with sets of additional phantoms, represent the population variability of individual skeletal bones and take sex differences into account. The developed phantoms can be used for internal dosimetry of osteotropic beta-emitters, including as part of radiopharmaceuticals.
REGENERATIVE MEDICINE
Introduction. Alginate is a natural polysaccharide that shows promise as a non-toxic material for the development of hydrogel wound dressings. Natural amino acids such as arginine and lysine are important components in the synthesis of the extracellular matrix and other vital bodily processes.
Objectives. Development of alginate gels modified with arginine and lysine and compatible with dermal fibroblasts. Study the release rate of these amino acids from the gel.
Materials and methods. The study was performed using three types of aqueous solutions of 3% sodium alginate containing arginine or lysine in amounts of 5, 10, and 20% of the alginate dry weight. To assess the stability of lysine gels over time, they were incubated for 1, 3, and 7 days in 600 µL of water at room temperature. The intensity of amino acid release from the alginate gel was evaluated by the spectrophotometric method after the reaction of ninhydrin. The DF2 cell line (human dermal fibroblasts, the shared research facility “Vertebrate cell culture collection” RAS) was used as model objects. Human dermal fibroblasts were cultured on the gels obtained. The cells cultured on the gels were evaluated using optical microscopy. Statistical analysis was performed using Microsoft Excel software; Student’s t-test was used to evaluate the differences between the samples. The differences were considered statistically significant at p < 0.05.
Results. On the first day, the gel containing the minimal lysine concentration of 5% showed the amino acid release of almost 16% of its initial amount. A more prolonged incubation of the gel led to a decrease in the desorbed lysine proportion relative to the initial amount. Statistically significant differences were obtained between the samples of alginate gels with the lysine content of 5 and 20% (p < 0.05). An increase in the lysine proportion in the gel was associated with a decrease in its release, i.e., the higher concentration of lysine the gel contained, the less amount of lysin was detected after seven days of incubation. It was shown that when a gel sample with a lysine content of 5% was incubated in a large volume of water (the gel-to-water ratio of 11%), more than 40% of lysine was desorbed into water during the first hour of incubation. Therefore, lysine was 4.3% more intensively desorbed from the alginate gel compared to the arginine gel. The following pattern was established: a twofold decrease in the amount of lysine release under an increase in the gel-to-water ratio from 11% to 20%.
Conclusions. During the study, alginate gels modified with amino acids were obtained. It was found that the higher the concentration of an amino acid in the gel, the less intensively it leaves the gel. The rate of amino acid release from the gel is directly proportional to the volume of liquid in which the gel was incubated. Human dermal fibroblasts adhered better to alginate gels modified with amino acids compared to cells on alginate gels without modification. As a result of the study, gels with controlled desorption of amino acids were obtained, which promote the adhesion of human dermal fibroblasts.
SURGERY
Introduction. Treatment of ulcer gastroduodenal bleeding is a challenging problem of emergency surgery. The combined technique of endoscopic hemostasis in ongoing arterial ulcer bleeding reduces the rate of recurrences in only 21.3% of cases, which indicates the need for improved endoscopic hemostasis technologies. In this regard, the use of triple therapy based on conventional methods (injections, coagulation, clipping) and local hemostatic systems seems promising.
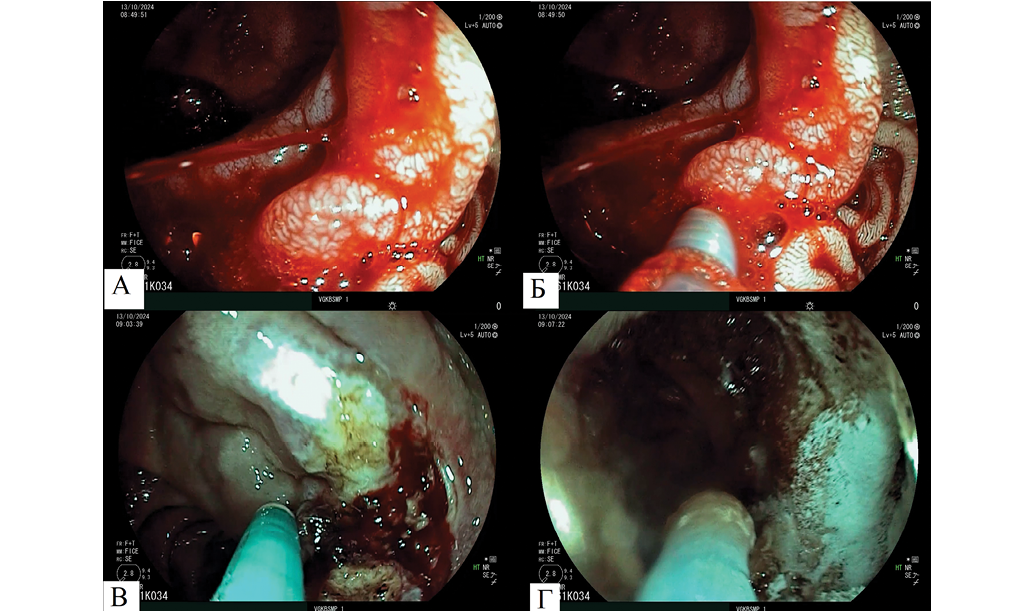
Clinical case description. We describe a clinical case of ongoing arterial ulcer bleeding from a peptic ulcer of gastroenteroanastomosis treated by endoscopic hemostasis using a 5% solution of aminocaproic acid with adrenaline in combination with argon plasma coagulation and pneumatic insufflation of an alginate polymer polysaccharide hemostatic hydrogel on the bleeding site.
Conclusions. The use of a personalized approach to endoscopic hemostasis of arterial bleeding from peptic ulcer of gastroenteroanastomosis using an alginate polymer polysaccharide hemostatic hydrogel as part of combined therapy improves the treatment outcome by ensuring final hemostasis, avoiding emergency surgery for massive bleeding, and facilitating the healing process of the ulcerous defect.
SPORTS MEDICINE
Introduction. The increase in the number of patients with post-acute sequelae of COVID-19, including athletes, requires improved diagnostic methods for the long-term effects of this disease. The study of changes in the blood-clotting sequence and immune regulation in a limited but homogeneous group of athletes (intense physical activity and careful health monitoring) with post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 can contribute to identification of reliable diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers of this condition.
Objective. A comparative analysis of the cytokine profile and hemostasis system features as promising prognostic markers for the diagnosis of post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 in athletes.
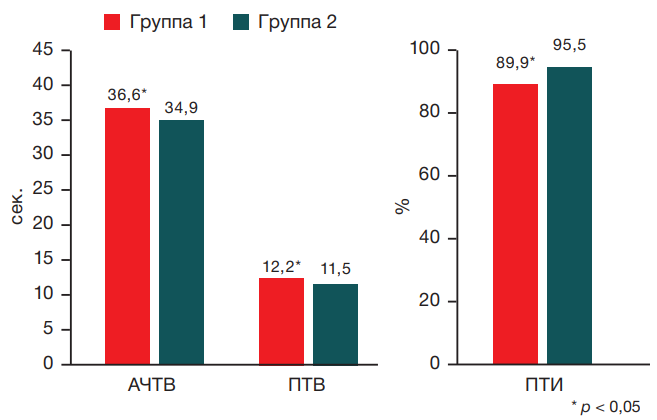
Materials and methods. 60 athletes (24 men and 36 women, average age 20.8 ± 1.86 years) were examined. All participants were divided into two groups: group 1 — 40 athletes who had suffered from coronavirus infection; group 2 (control) — 20 athletes who had not had COVID-19. The athletes specialized in various sports: figure skating, rhythmic gymnastics, athletics, rugby, and wrestling. To assess the residual effects of COVID-19, biochemical parameters were studied in all participants: alanine aminotransferase activity, aspartate aminotransferase, C-reactive protein level, troponin-I level; hemostasis parameters: prothrombin time (PT), prothrombin index (PTI), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), international normalized ratio (INR), D-dimer; immune status indicators: interleukins-6, -8, -10 (IL-6, -8, -10, respectively), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). Statistical data processing was carried out using the Statistica 10 software.
Results. An increase in clotting time was revealed in terms of aPTT, prothrombin time, international normalized ratio, and a decrease in the prothrombin index (p < 0.05). Statistically significant differences in the functional state of the immune system were also found: an increase of IL-8 from 2.5 to 7.42 times [3.08; 9.96] pg/mL and IL-10 from 2 to 5.08 times [2.93; 6.66] pg/mL compared to similar indicators in athletes who had not suffered from COVID-19 — 3.05 [1.86; 8.15] pg/mL and 2.53 [1.0; 5.68] pg/mL (p < 0.05) in the group of athletes who had undergone COVID-19. A direct correlation was established between an increase in IL-8 levels and an increase in PT (rs = 0.355; p < 0.05) and INR (rs = 0.420; p < 0.05) in athletes who had undergone a coronavirus infection. At the same time, a negative association was found between an increase in IL-8 levels and a decrease in PTI (rs = –0.323; p < 0.05).
Conclusions. Higher levels of activating cytokines and lower values of parameters of the anti-inflammatory immune system indicate residual dysregulatory phenomena in the immune system in post-acute sequelae of COVID-19. The revealed relationships between the coagulation profile and the components of the immune response allow these relationships to be considered as possible diagnostic markers of residual phenomena after coronavirus infection. The data obtained confirm the validity of IL-8 and IL-10 indicators as potential markers of residual disorders after COVID-19 in athletes. However, these findings should be verified on larger samples, where the observed ratios may show a different dynamics.
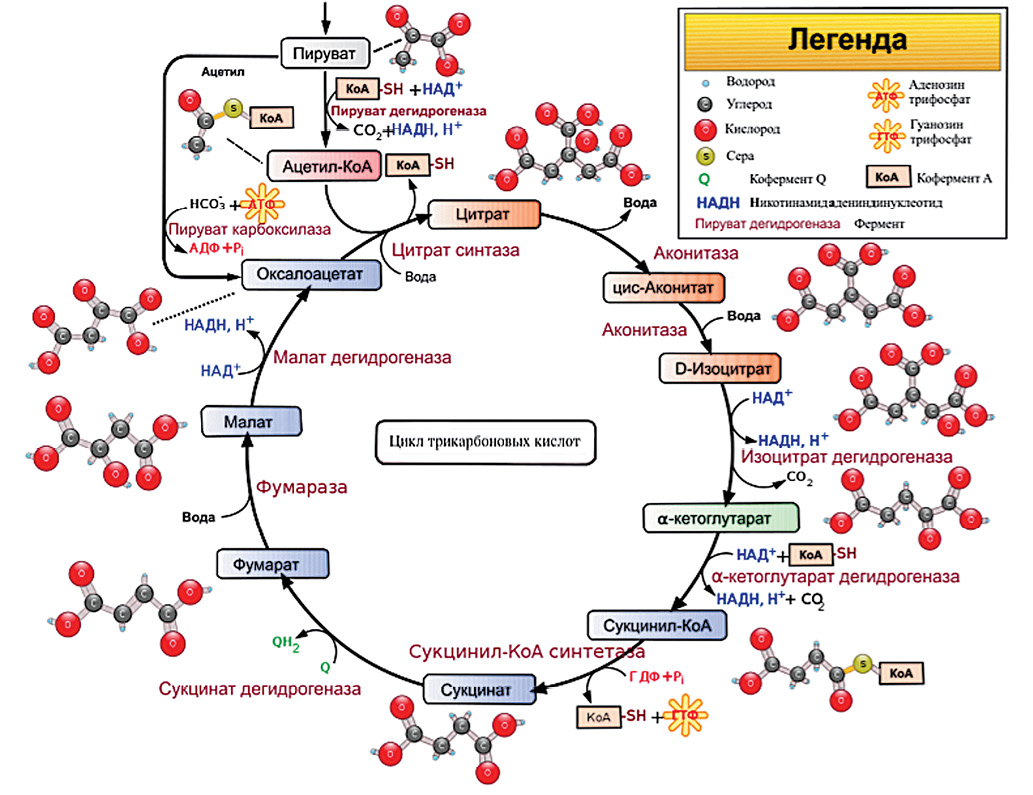
Introduction. Various metabolites of the tricarboxylic acid cycle (Krebs cycle, TCA cycle, TCAC) find application in medicine. The emergence of improved chemical synthesis methods and the more affordable production of individual TCA metabolites make them promising candidates for developing effective compositions capable of increasing the adaptive potential of the human body.
Objective. Identification of the physiological effects of the main TCA metabolites. This knowledge is important for informed application of TCA metabolite-based products in the medical and biological support of athletes.
Discussion. The conducted literature review investigated the physiological effects of TCA metabolites — energy metabolism substrates — used in sports medicine. At present, succinate, citrate, malate, and oxaloacetate have found reasonable use. A number of publications have reported the anti-catabolic effect of alpha-ketoglutarate; however, the current level of evidence is insufficient. Isocitrate dehydrogenase is promising for use in sports medicine, which substantiates its further detailed study.
Conclusions. Due to their physiological effects, the majority of TCA metabolites can be used in the compositions of antihypoxic, antioxidant, neuroprotector, and metabolic correction agents. A number of TCA metabolites are promising substances for creating new products for the medical and biological support of athletes, which validates additional research of their physiological effects.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Introduction. Acinetobacter baumannii (A. baumannii) is a widespread and exclusively hospital-acquired microorganism whose new mutation is resistant to most available antibiotics, with the exception of tigecycline. Clinicians are concerned about recent evidence of resistance to this antibiotic in Iran.
Objective. This study evaluates the resistance of Acinetobacter baumannii (A. baumannii) to tigecycline in Iran, considering its clinical significance in treating multi-drug-resistant infections.
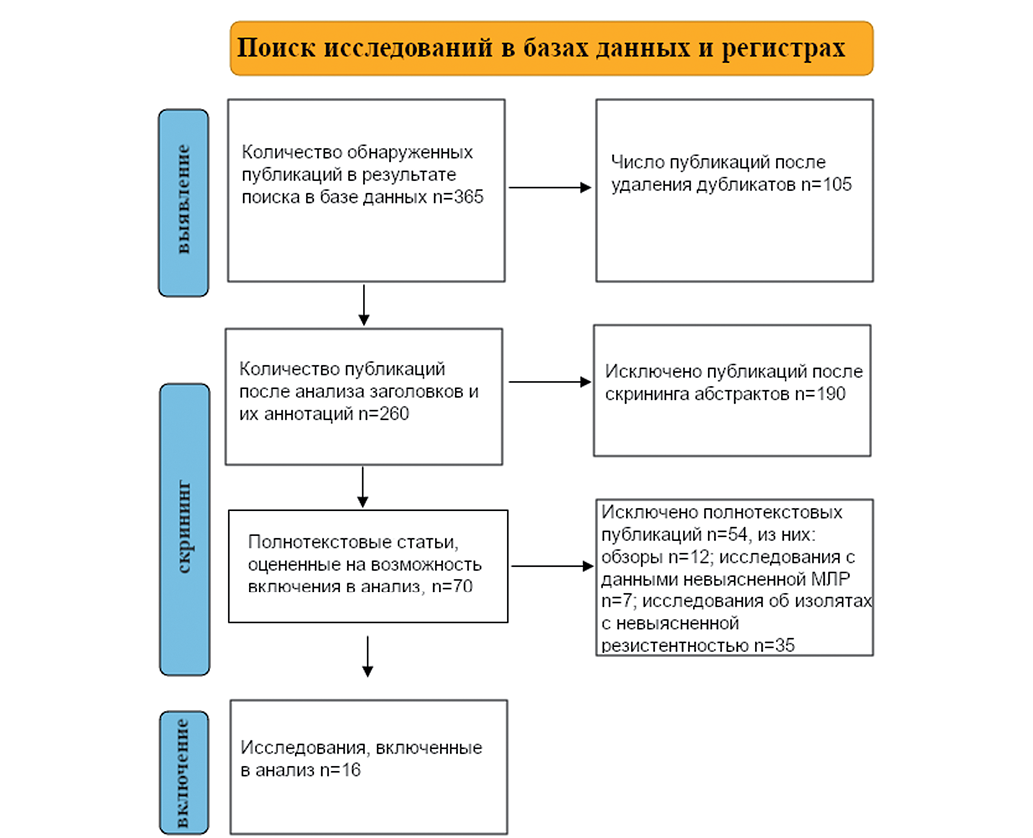
Methods. The MEDLINE, PubMed, Web of Science (WOS), and Scopus databases were searched for studies published over all this time to January 2024. The advanced search using Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terms for “Acinetobacter baumannii” and “Tigecycline” was performed. The title, abstract, and full text of the articles were screened based on eligibility criteria. The cross-sectional studies reporting Tigecycline resistance in sequential isolates of A. baumannii in patients admitted to the hospitals in Iran were included.
Results. A total of 16 studies were included for meta-analysis. The overall prevalence of A. baumannii strains resistant to tigecycline in Iran equals 18.1%. Among the reviewed studies, distinct variances of resistance were detected. Although investigations were conducted in limited regions, the studies reported a wide range of resistance in Tehran (0%) and in Tabriz (100%) as minimum and maximum, respectively.
Conclusion. Despite the high level of resistance in some cities of Iran, tigecycline is still one of the most effective antibiotics for the treatment of A. baumannii infection. Improved control over the use of antibiotics may contribute to hampering the spread of resistance to these agents.
ISSN 2713-2765 (Online)