RADIOBIOLOGY
Introduction. The influence of radiation-induced genetic instability on the formation of clonal expansion is a relevant problem in health monitoring and preventive diagnostics of oncohematological and somatic pathology in individuals exposed to long-term low-dose anthropogenic irradiation, such as nuclear industry workers and radiation diagnostics doctors.
Objective. Identification of possible application points of preventive diagnostics of genome instability markers and clonal hematopoiesis in groups of individuals exposed to long-term low-dose anthropogenic irradiation.
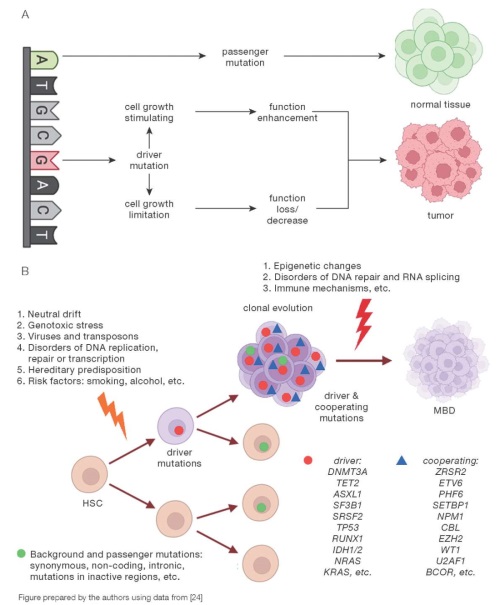
Results and discussion. Genetic instability in genes of epigenetic regulation (DNMT3A, TET2, ASXL1), signaling pathways and cell proliferation (JAK2, FLT3), DNA repair regulators (TP53, PPM1D), RNA splicing factors (SF3B1, SRSF2) most often initiates clonal hematopoiesis, which is realized more frequently by myeloid and less frequently by lymphoid neoplasia. The influence of clonal hematopoiesis on the development of somatic diseases is mediated by the combined effect of carrying these mutations and the processes of chronic inflammation. Low-dose ionizing radiation is capable of initiating clonal expansion mainly due to mutations in DNMT3A and TET2 genes. There is a lack of studies on the assessment of increased morbidity against the background of clonal hematopoiesis in groups of occupational risk of low-dose ionizing radiation exposure (workers in the nuclear industry and doctors of radiation diagnostics), which requires further study.
Conclusions. Studies aimed at identifying risk markers of morbidity growth in the setting of clonal hematopoiesis in groups of workers exposed to long-term anthropogenic action of low-dose ionizing radiation form the basis for developing cohort-oriented programs of disease prevention in these individuals.
EMERGENCIES SAFETY
Introduction. The methodology for assessing health threats and risks is becoming increasingly in demand in the public management of the sanitary and epidemiological welfare of the population. New biomedical, predictive analytical, and mathematical approaches are being developed to assess and analyze health threats and risks in emergencies, including within biological risk monitoring. These issues require a scientifically based comprehensive consideration drawing on various scientific fields, including medicine, biology, management, prediction, sociology, and mathematics (probability theory, set theory, measure theory, etc.). To solve this problem, the authors adopted a convergent approach, paying special attention to the role of effective threat and risk management, which has a significant impact on the quality of life of people exposed to adverse factors in emergency situations.
Objective. To improve the technology for analyzing and predicting threats and risks to human health in emergencies using a convergent multidisciplinary approach.
Materials and methods. The authors searched electronic bibliographic databases in the Russian (eLibrary and CyberLeninka) and English (Web of Science, Scopus, PubMed, Google Scholar, and Cochrane Library) languages. The database “Regulatory Legal Acts on Radiation, Chemical, and Biological Monitoring” created at the Centre for Strategic Planning of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency served as the basis for analyzing regulatory documents. As the information platform in this study, the authors used the information system of the Federal Information and Analytical Center for Monitoring Biological Risks, which aggregates data on the monitoring of biological risks falling within the competence of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency, The predictive and analytical part of the study was scientifically justified using the database “Methods of Scientific Prediction” created at the Centre for Strategic Planning, which contains systematized methodological prognostic information. The theoretical methods used in the study include logical methods (analysis and synthesis of knowledge; analogy method), mathematical methods (modeling, probability theory, measure theory, graph theory, and set theory), and the method of theoretical generalization.
Results. In the study, the existing approaches to assessing health threats and risks arising in emergency situations are summarized and systematized; their main characteristics and key parameters are considered. The phases of the process involving the emergence of threats and risks to health and the specifics of their management are analyzed. The scientific medical and biological point of view on the essence and general characteristics of health threats and risks is presented. The predictive analytical and mathematical aspects of the problem under consideration are outlined. An example algorithm for predictive and analytical calculation of indicators characterizing the resource capability and readiness of the healthcare system to adequately respond to a biological threat is described in detail. The required bed capacity of medical organizations is assessed, as well as the need for artificial lung ventilation devices in case of an epidemic; the final values are calculated. The analysis of the specified issues using a comprehensive convergent approach creates the prerequisites for effective management of health threats and risks in emergency situations.
Conclusions. Predictive and analytical approaches are based on advanced ideas and mechanisms, including risk-based technologies, digital certification of territories and objects, active use of geoinformation developments, assessment procedures drawing on the combination of estimated and field data, situation modeling under changing or specified conditions, consideration of combined impact factors, etc. Characterizing the risk through a health hazard measure that combines the probability of health threats occurring in an emergency and the consequences of adverse effects for life and health, the authors define the value of risk as the mathematical expectation of the product of a function for assessing damage (consequences) to the health of an organism/population and the probability of combined impact of adverse factors in an emergency.
IMMUNOLOGY
Introduction. Allergic diseases are a pressing challenge in practical healthcare, attracting increased attention of various medical specialists. The pathogenesis of stress-induced urticaria is driven by neurogenic immune inflammation, accompanied by an increase in the level of neuropeptide substance P (SP).
Objective. Assessment of the relationship between stress factors and substance P levels with the purpose of justifying the use of SP as a biomarker for assessing the clinical course and prognosis of the disease in patients with chronic urticaria.
Materials and methods. The study was involved 165 adults aged 18–68 years. The main group included 97 patients with the confirmed diagnosis of chronic urticaria (CU) who were treated in a hospital setting in the period from 2018 to 2023. The comparison group included 68 practically healthy individuals, comparable in gender and age with the study group of patients. The level of substance P in the blood serum was estimated by immunoenzymatic techniques (Infinite F50 Tecan, Austria), using a CEA393Hu test system. Statistical processing of the results was performed using the STATA 18 software package (StataCorp LLC).
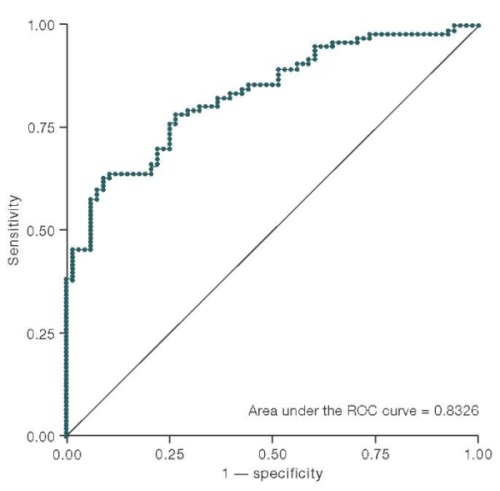
Results. An increase in the production of substance P to 220.62 pg/mL in CU patients, compared to 96.57 pg/mL in the reference group (p < 0.001), was observed. The logistic regression revealed an association between stress and substance P levels in CU patients. Thus, an increase in the concentration of substance P by 1 pg/mL led to a 1.02-fold increase in the CU risk. The CU risk increased by 3 times in the presence of a stress situation as a trigger.
Conclusions. The constructed multivariant logistic regression model produced positive values of the model parameters (p ≤ 0.01). This indicates the correlation between the increased blood levels of substance P under the impact of stress factors and the risk of chronic urticaria development. The data obtained suggests that the concentration of substance P in the blood of CU patients can be considered as a potential diagnostic biomarker. This biomarker can be recommended for extending panel screening tests to clarify the pathogenesis of the disease, thus improving the differential diagnosis of the disease and facilitating early detection of patients with stress-induced urticaria.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Introduction. The development of improved formulations of antidotes and remedies, which can be used not only by qualified medical personnel, but also in self- and mutual assistance, is an urgent task for extreme medicine.
Objective. Evaluation of the possibility of using nanoscale polymer delivery systems for medicines and antidotes intended for intranasal administration (into the nasal cavity) in extreme medicine.
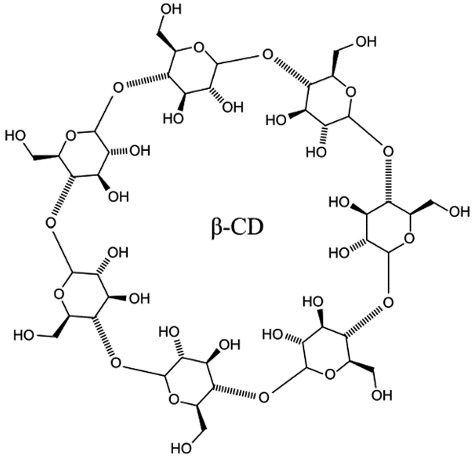
Discussion. The main submicron-sized polymer carriers which are promising as the basis for the creation of an intranasal form of antidotes are identified. The bioavailability of the substance delivered is dependent on the physico-chemical properties of the carrier, the conditions for its production, as well as physiological and anatomical factors. Data is presented regarding possible ways of correcting these factors in order to increase bioavailability. Examples of the use of polymer nanocarriers in the treatment of poisoning with heavy metals and rocket fuel components, as well as lesions caused by radioactive substances, are presented. It is shown that carriers (dendrimers, cyclodextrins) can act as antidotes in certain cases. The study presents a list of antidotes approved for use within the territory of the Russian Federation, for which the development of intranasal forms is possible, taking their physico-chemical and pharmacokinetic properties into account.
Conclusions. Following a review of literature sources, the most promising submicron-sized polymer carriers for the intensification of intranasal delivery of drugs and antidotes are herein proposed: dendrimers, liposomes, nanocapsules, nanoparticles, and cyclodextrins. Using the list of antidotes approved for use in the Russian Federation as an example, promising drugs that can be potentially developed on the basis of these carriers are proposed.
Introduction. Carbamates are widely used in the pharmaceutical industry, agriculture, and household chemicals. Being reversible cholinesterase inhibitors, carbamates can cause the development of generalized convulsive syndrome. Untimely treatment contributes to the emergence of persistent neurological disorders. In order to develop and adequately assess in preclinical studies the specific activity of new drugs for the relief of convulsive syndrome in acute intoxication with this group of substances, an easily reproducible experimental model of convulsive carbamate-induced syndrome is required.
Objective. Development of an experimental model of generalized convulsive syndrome in rats using phenylcarbamate as a model toxicant for testing in preclinical studies of therapies for poisoning with cholinesterase inhibitors.
Materials and methods. The study was performed using mongrel sexually mature male rats, aged 3 months (80 animals), divided into 4 groups (3 experimental and 1 control). At the first stage, the parameters of convulsive syndrome caused by model toxicants were compared: phenylcarbamate 1 mg/kg bw, corazol 65 mg/kg bw, and thiosemicarbazide 8 mg/kg bw. The following parameters were studied: motor activity (open field test), neuromotor functions (grip strength test), cognitive functions (conditioned avoidance responses, CAR), and cardiovascular indicators (ECG and cardiac rhythmogram assessment). The severity of the convulsive syndrome was identified by Racine stages. Additionally, the structure of brain tissues was evaluated by histological methods. second stage, biochemical parameters were studied in three experimental (with toxicants) and control groups. Some biochemical parameters were studied in the blood serum, assessing the function of the liver, kidneys, prooxidant and antioxidant systems. At the third stage, the activity of cholinesterase in the blood and brain was studied in 30 control and 30 experimental rats after phenylcarbamate exposure. Statistical processing of the results was carried out using Statistica v.10.
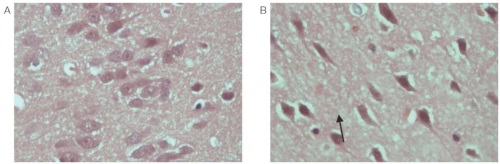
Results. When modeling convulsive syndrome in rats, phenylcarbamate is comparable to corazol in terms of the onset of the latency period, duration and intensity of seizures. When implementing the model, a significant decrease in heart rate was recorded 48 h after administration. The CAR test found that the introduced substance increases the time of the first entry into the dark compartment before training. Significant changes in markers of liver function (ALT, bilirubin, cholesterol, triglycerides), lipid peroxidation and the antioxidant system (MDA, GPx) confirm the complexity of mechanisms responsible for the development of seizures and neurological disorders. The results of histological examination of brain tissues indicate that phenylcarbamate induces pronounced disorders of the brain structure in an experiment on rats.
Conclusions. The developed experimental model of phenylcarbamate-based convulsive syndrome in rats is easy to reproduce, thus being recommended for preclinical studies of new drugs for the relief of convulsive syndrome in poisoning with cholinesterase inhibitors.
TOXICOLOGY
Introduction. Hemostasis of ongoing bleeding during cavitary surgical interventions is an urgent problem both in civil and military healthcare. The development of new effective and affordable agents for hemostasis of internal bleeding and their introduction into clinical practice may contribute to increasing the survival of injured patients.
Objective. Study of general and local toxic effects of a local hemostatic agent (LHA) for intracavitary application.
Materials and methods. The study was performed on 20 mongrel rats (10 males and 10 females) weighing 180–220 g. The experimental group of animals was implanted with the LHA into the abdominal cavity at a dose of 512 mg/kg body weight (bw). The animals of the control group underwent surgery without LHA implantation. Data analysis was performed using the Microsoft Excel 2013 and Statistica 10.0 software applications.
Results. The health status, body weight, food and water consumption, and mass coefficients of internal organs in the experimental animals did not differ from those in the control group. The hematological and biochemical blood parameters showed values within the reference norm. The macro- and microscopic examination of the internal organs revealed a local irritant effect of the agent under study.
Conclusion. The laboratory animals tolerated the intraperitoneal implantation of the tested local hemostatic agent at a dose of 512 mg/kg bw well. A further study of its toxic properties and effectiveness is validated.
MICROBIOLOGY
Introduction. Klebsiella pneumoniae poses a serious threat to global healthcare due to the high proportion of multidrug-resistant isolates. Moreover, the formation of biofilms by bacteria significantly complicates the treatment of infections.
Objective. To evaluate the effectiveness of the individual and combined action of antibiotics and bacteriophages or polysaccharide depolymerase on biofilms of a clinically significant strain K. pneumoniae.
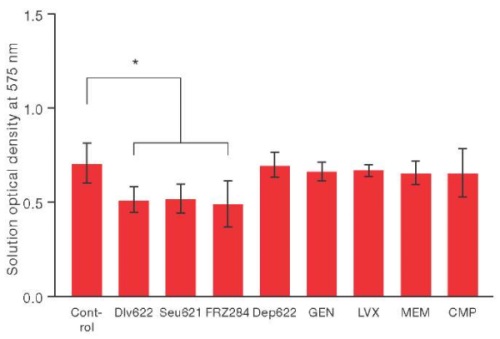
Materials and methods. The work used the K. pneumoniae strain with multidrug resistance (9faiz), 4 antibiotics of various classes (gentamicin, levofloxacin, meropenem and chloramphenicol), 3 bacteriophages of various genera (Dlv622, Seu621 and FRZ284), and 1 polysaccharide depolymerase (Dep622). Experiments were carried out on the formed biofilms by treating 24-hour K. pneumoniae films with antimicrobial agents individually or in combinations. The ability of the strain to form biofilms was evaluated by staining with crystalline violet. The comparison between the average optical density values was carried out using a t-test and was considered significant at p ≤ 0.05.
Results. The individual use of antibiotics peak concentrations (Cmax) or depolymerase concentration of 100 MED (minimum effective dose — MED) did not lead to a significant decrease in biofilm biomass, whereas bacteriophages in a titer of 5×109 PFU/mL (plaque-forming unit per mL) statistically significantly reduced its biomass by 27–31% (p < 0.05) Most combinations of phages and antibiotics did not lead to a significant increase in the efficiency of biofilm destruction. Only the combination of phage FRZ284 with gentamicin statistically significantly showed an additional decrease in biofilm biomass by 27% (p < 0.05).
Conclusions. The results show the need for individual selection of antimicrobial combinations to combat K. pneumoniae biofilms due to the possible effect of synergy and antagonism effects on the outcome of therapy.
PREVENTIVE MEDICINE
Introduction. Preservation of the health and professional longevity of people of working age is a priority task of the Russian healthcare system. In this regard, it is extremely important to study the structure and dynamics of occupational pathology for the scientific justification and development of measures aimed at managing the risks to the health of workers in enterprises with extremely dangerous working conditions and to prevent the development of occupational diseases.
Objective. To study specific features in the structure of occupational morbidity of workers of a uranium mining enterprise over a 50-year period.
Materials and methods. The work was performed on the model of a large uranium mining enterprise within the Rosatom State Corporation in Russia with extremely dangerous working conditions. Cases of occupational diseases detected in workers from the beginning of the operation of the company from 1970 to 2019 were analyzed. The structure of occupational diseases was characterized, and the share contribution of the main nosological forms over 5-year periods was analyzed.
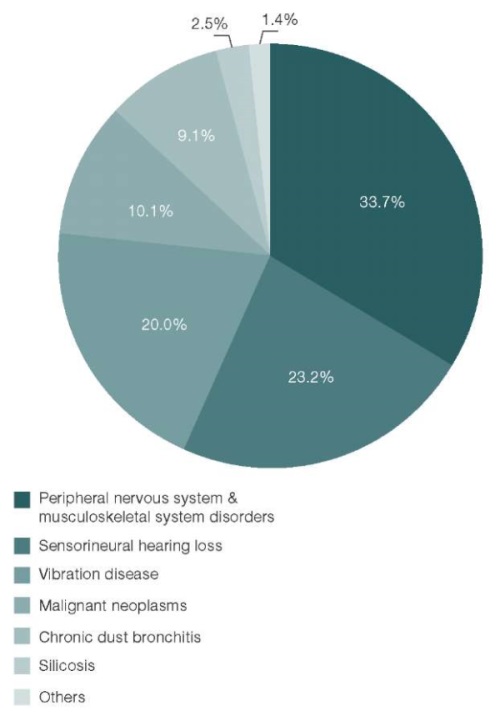
Results. The main nosological forms of occupational diseases in underground miners of a uranium ore mining enterprise were identified. A steady trend towards an increase in the total number of cases of diseases was noted. There was a gradual increase in the proportion of diseases of the musculoskeletal system and peripheral nervous system, a decrease in the proportion of “dust” pathology, an increase and subsequent decrease in the proportion of sensorineural hearing loss, as well as a stable contribution to the structure of occupational pathology of malignant neoplasms.
Conclusion. Indicators of a priori occupational health and safety risk of uranium mining workers reflect the levels of their occupational morbidity. Musculoskeletal system disorders and occupational malignancies dominate in the structure of occupational diseases. This morbidity is many times higher than the national average.
Introduction. Gene-targeted therapies (gene-targeted, high-tech, and biopharmaceuticals) are developed based on active pharmaceutical ingredients, which are reactive compounds with pleiotropic activity. Such ingredients are associated with health hazards to workers employed at various stages of their production. Clinically significant pharmacological or toxicological effects of innovative medications on employees exposed to these components are unsafe from the perspective of a risk-based approach in occupational medicine.
Objective. Assessment of potential risks of occupational exposure to innovative biopharmaceuticals in production or laboratory conditions and approaches to their hygienic management.
Materials and methods. The relevant scientific publications were searched and retrieved via electronic bibliographic databases both in the Russian language (eLibrary, CyberLeninka) and in the English language (WoS, Scopus, PubMed). Regulatory documents were analyzed using the Consultant Plus legal information system.
Discussion. Specific features of production of new-generation biopharmaceuticals (gene-targeted, high-tech, or biotechnological medications) and the associated risks of occupational exposure to workers in pharmaceutical or laboratory production are considered. It was established that employees of such enterprises are exposed to the combined influence of adverse — biological, physical, and chemical — production environment factors. There is a lack of information on the development of analytical methods for identifying gene-targeted components (high-tech or biotechnological medications) in the workplace air and wastewater, as well as on workplace surfaces. The identified problems of occupational health are related to the lack of legislative instruments and knowledgebased management decisions on the identification of risk factors and control ranges of potential work-related effects of innovative biopharmaceuticals. Such approaches should be based on the principles of hygienic regulation aimed at eliminating or reducing negative industrial effects and ensuring the safety and preservation of employee health.
Conclusions. Major methodological approaches to assessing the work-related impact of gene-targeted, high-tech, or biotechnological therapies on employees of pharmaceutical enterprises are determined. These approaches include: (1) toxicological assessment of compounds with the establishment of possible parameters of toxicometry; (2) evaluation of the pharmacological and toxicokinetic features of gene-targeted therapeutical components; (3) development of methods for their quantitative determination in various environments; (4) establishment of biomarkers of exposure and related effects followed by hygienic rationing and justification of preventive measures.
Introduction. Suspension trauma, also referred to as a harness-induced pathology or suspension syndrome, occurs when an individual is suspended motionless in a harness. Potentially fatal outcomes of such a condition consist in venous pooling, cerebral hypoperfusion, and rhabdomyolysis.
Objective. To review literature sources on the key mechanisms of suspension injury and potential methods for improving the safety of people at risk.
Results. This condition, recognized since the 1970s, affects individuals involved in activities requiring harness use, such as climbing and industrial work. Recent studies have emphasized the need for immediate horizontal positioning during rescue to restore blood flow and prevent complications. Proper management of hyperkalemia and rhabdomyolysis has become a crucial focus in treatment protocols. Additionally, recognition of the role of the Bezold–Jarisch reflex in cardiovascular collapse highlights the importance of comprehensive rescue strategies. Advances in harness design are also noted as significant preventive measures.
Discussion. The findings indicate that while early management strategies focused on preventing sudden blood return to the heart by maintaining an upright position, more recent insights emphasize the importance of prompt horizontal repositioning. The role of neurocardiogenic factors, such as the Bezold–Jarisch reflex and the influence of rhabdomyolysis-related hyperkalemia, on outcomes has been recognized. This shift reflects an increased awareness of comprehensive rescue protocols that might mitigate risks associated with reflow syndrome and cardiovascular instability.
Conclusions. The progress in understanding suspension injury has significantly improved prevention and treatment protocols. Immediate adjustment of the victim to a horizontal position, proper treatment of complications (for example, hyperkalemia), and improved design of safety systems — all play a key role in minimizing deaths. Further studies should be aimed at investigating the main pathogenetic mechanisms of suspension syndrome and development of advanced rescue methods for improving the safety of people at risk.
CLINICAL MEDICINE
Introduction. Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer mortality in men and women. Due to its high prevalence and significant recurrence rate after standard therapy, the search for new methods of lung cancer treating is an urgent task. A promising treatment strategy is immunotherapy that elicit immune response against tumor cells.
Objective. Evaluation of the clinical efficacy and prospects for the safe use of immunotherapy in malignant neoplasms of the pleural cavity.
Discussion. The introduction of immunotherapeutic approaches, including adoptive cell therapy with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) or CAR-T cells, the development of neoantigen vaccines, oncolytic viruses, in combination with chemotherapy and blockade of immune checkpoints (ICP) have shown optimistic results in preclinical studies and are currently at different stages of clinical trials for safety and efficacy.
Conclusions. Immunotherapy of lung cancer is a promising area of adjuvant therapy. For clinical introduction, immunotherapeutic approaches should be further investigated to increase their effectiveness and minimizing side effects by combining different therapies, improving bioengineered and cellular drugs, and reducing the cost of treatment.
MARINE MEDICINE
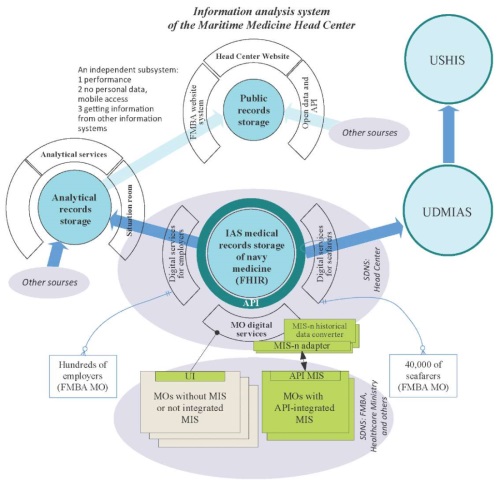
Introduction. Managing the process of collecting, analyzing, and systematizing the results of medical examinations of seafaring personnel in medical organizations of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency (FMBA) of Russia requires development of a specialized information system.
Objective. To carry out a comprehensive analysis of the activities of FMBA organizations, to develop on its basis and implement into practical use an information system for ensuring the continuity of all types of medical support for seafaring personnel; to create a digital Register of the results of medical examinations of seafarers.
Materials and methods. During the 2014–2023 period, the principles of organizing the work of medical organizations that provide medical care to seafaring personnel were studied. A methodology for recording the results of medical examinations of seafarers with the purpose of forming an information Register was developed. An analysis of medical support provided to people working on ships in 2023 was conducted based on the reports of FMBA structural units, including 35 health centers, 70 ship doctors, and 14 doctors of diving medicine.
Results. In March 2023, the Head Center for Health Protection of Seafarers, FMBA, implemented a pilot project on creation of a Register in the Northwestern Federal District. Within its framework, a methodology for generating a seafarer identification number in the Register was developed and 26,125 records of information about persons who underwent preliminary and periodic medical examinations were analyzed. The implementation of the proposed methodology for the formation of registers in all districts allowed an information system in the amount of 38,993 conclusions to be drawn based on medical examinations conducted in 2022–2023.
Conclusion. A single informational resource in conjunction with the Register for all 35 medical organizations that provide medical support to seafaring personnel, including conducting preliminary and periodic medical examinations, forms the basis for further improvement of scientific approaches to the organization and development of maritime and diving medicine in the Russian Federation.
SPORTS MEDICINE
Introduction. The vast majority of modern sports exert a significant load on the musculoskeletal system (MSS). The ever-growing popularity of sports among underage children, their active participation in various competitions and trainings impose an increased risk of sports injuries, particularly minimal trauma and injury of large joints. Although numerous works have addressed the development of clinical diagnostic and therapeutic methods used for MSS injuries, there is a lack of publications on sports injuries in underage athletes.
Objective. Evaluation of current methods for diagnosis and therapy of minimal trauma and injury of large joints in underage athletes with the purpose of selecting the most promising and effective methods.
Findings. The main causes and mechanisms of injuries are considered. Such injuries are generalized depending on the sports type. A review of available methods for clinical and instrumental research and innovative therapeutical methods is carried out. Platelet-rich plasma therapy (PRP) was found to be the most promising minimally-invasive biotherapy for MSS injuries, particularly with respect to children and adolescent athletes. This method restores the anatomical integrity of damaged elements and relieves pain at rest, during physical exertion, and in a stress test with the possibility of preserving the function of the injured joint and rehabilitation in the shortest possible time. PRP therapy is an alternative to conventional treatment methods, offering new prospects in regenerative and sports medicine.
Conclusions. A comprehensive personalized approach combining clinical examination and instrumental studies is key to ensuring the accuracy and objectivity of the health status of young athletes. Such an approach allows diseases to be identified at an early stage, differential diagnosis to be conducted, and treatment efficacy to be evaluated, taking the specifics of pediatric practice into account.
SPACE MEDICINE
Introduction. The increasing duration of spaceflights and the associated prolonged exposure of space crewmembers to unfavorable microgravity conditions necessitate the development of improved approaches to diagnosing the health status directly during the flight. This study is aimed at searching and selecting promising biological markers suitable for studying directly during spaceflights.
Objective. To review the current status of the abovementioned problem and to identify biochemical and molecular markers most promising for biomedical research in spaceflight conditions.
Methods. A literature review of methods currently used for monitoring the level of biological markers characterizing variations in the immune, excretory, reproductive, musculoskeletal, and blood coagulation systems caused by spaceflight conditions was carried out.
Findings. Data concerning biological markers used for monitoring the health status of space crewmembers were analyzed. The authors argue that protein markers reflecting bone tissue remodeling hold particular promise. The decrease in bone tissue density developed as a result of microgravity carries potential risks of traumatism, thus making screening diagnostics of the state of the musculoskeletal system a key focus of laboratory diagnostics. The conducted literature review suggests that P1NP and osteocalcin may serve as the most informative markers of new bone tissue formation, while collagen C-telopeptide, pyridine cross-links, and tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase may serve as markers of bone tissue lysis.
Introduction. Human intestinal microflora fulfils a wide range of important functions for the body. It provides non-specific anti-inflammatory defense through the production of bacteriocins, organic acids and substances with bacteriostatic properties. It also stimulates eukaryotic cells to synthesize mucin and substances with antimicrobial activity, thus suppressing the development of inflammatory reactions in intestinal epithelial cells. These bacteria obviously act synergistically with immunocompetent intestinal cells undergoing changes in zero gravity conditions modeled using dry immersion. Regulatory and metabolic changes which occur during model experiments are reflected, inter alia, in the protein composition of the blood.
Objective. Identification of the relationship between the blood protein level and the amount of E. coli, Lactobacillus spp., Enterococcus spp. and Bifidobacterium spp. in the intestine using an experimental model of 3-day dry immersion for potential use as clinical recommendations for the correction of intestinal microflora, based on data from the proteomic profile of the blood.
Materials and methods. The study was conducted among six women aged 25–40 years. During 3-day dry immersion, the subjects were completely immersed in an immersion bath containing water at room temperature. Direct contact between the subjects’ skin and the water was excluded. During the study, fecal samples and capillary blood samples were taken from each of the participants. In order to assess the protein levels, chromatography-mass spectrometric analysis of samples of dried blood spots was performed using nano-HPLC Dionex Ultimate3000 combined with a timsTOF Pro mass spectrometer. The study of the number of intestinal bacteria was carried out using culture seeding of pre-diluted fecal samples on selective media according to a standard technique, followed by consideration of colonies.
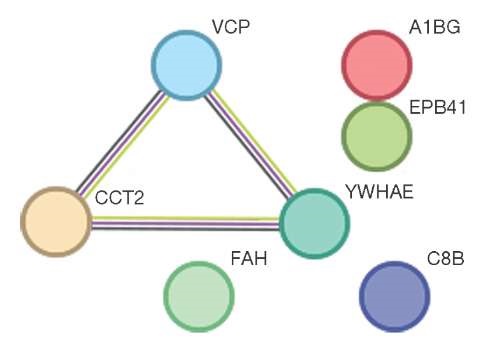
Results. The regression model showed a relationship between the levels of individual proteins and representatives of the intestinal microflora. A statistically significant correlation was found between blood proteins ENO1 (r = 0.71), MYH9 and SPTA1 (r = –0.99) with the amount of E. coli; blood proteins EPB41, VCP, C8B, CCT2 (r = 0.74), FAH, YWHAE (r = –0.46) with the amount of Bifidobacterium spp. There was also a significant strong positive correlation between Lactobacillus spp. and proteins ENO1, CA2 (r =0.74) and S100A6 and HSPA4 (r =–0.87). The CALM2 protein (r = –0.76) correlated with the amount of Enterococcus spp.
НEMATOLOGY
Introduction. Due to the increased requirement for platelet concentrate use in the treatment and prevention of thrombocytopathy, there is a pressing need for the development, improvement and implementation of new approaches to monitoring its quality parameters and safety assessment.
Objective. To conduct a systematic review and analysis of literature data, in order to identify promising approaches to evaluating an adequate analysis of the quality of platelet concentrate to improve the effectiveness and safety of transfusions.
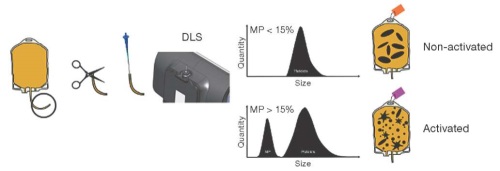
Discussion. The possibilities and advantages of a rational approach to platelet concentrate transfusion are established, while considering the degree of platelet activation required to optimize the preparation of the component. Special attention was paid to methods for evaluating platelet activation. The detection of microparticles based on dynamic light scattering will make it possible to distinguish activated platelets (with a high content of microparticles) from inactive (with a low content of microparticles) platelets during both therapeutic and preventive transfusions and optimize the use of this scarce blood component.
Conclusions. The ability to differentiate platelet concentrates based on the screening of the content of microparticles formed due to activation will contribute to improving the effectiveness and safety of transfusion therapy.
Introduction. Cryopreservation allows for long-term conservation of biomaterials. The insufficient efficacy of available cryopreservatives and the toxicity of a number of cryocomponents renders the search for low-toxic biocompatible cryoagents highly relevant.
Objective. Assessment of morphological and functional features of blood cells in a lactulose-based cryopreservative for storing whole blood at moderately low temperatures (minus 20 °C) using leukocyte, platelet, and erythrocytes parameters.
Materials and methods. The study was conducted using peripheral venous blood of 30 female donor volunteers aged 18–23 years. Samples of peripheral venous blood were stabilized by 3-substituted potassium salt of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. The cryopreservative was prepared using a 0.9 % sodium chloride solution to maintain the isotonic concentration. Glycerin and dimethyl sulfoxide were used as cell-penetrating cryoprotectors; lactulose disaccharide was used as a non-penetrating cryoprotector. The composition of the obtained cryopreservative was optimized by varying the mass fractions of the components. Clinical blood tests were performed using a Gemalite 1270 automatic hematology analyzer. A computer cytomorphometric study was performed in the MEKOS-C2 hardware and software environment.
Results. The conservation of blood samples using the developed cryopreservative for 24 h at a temperature of minus 20 °C increased the percentage of preserved leukocytes, erythrocytes, and platelets to 88.6±0.41 %, 92.1±0.31 %, and 91.4±0.52 %, respectively. The blood cells retained their physiological activity after thawing compared to blood samples stored at room temperature.
Conclusions. The morphological and functional safety of blood cells in samples stored with the developed cryopreservative was revealed after 24 h of storage at minus 20°C. The advantages of this cryopreservative include the possibility of its long-term storage without loss of cryoprotective properties, stabilizing blood cells to the effects of sub-moderate low temperatures of minus 20 °C, the use of non-toxic lactulose disaccharide that does not penetrate into the cell. The developed cryopreservative proves effective in freezing conditions at minus 20 °C, being affordable in terms of cost (all components are manufactured in the Russian Federation). Further research in this direction will contribute to the development of safer blood donation approaches and reducing complications during transfusion of blood components.
ISSN 2713-2765 (Online)