MAIN TOPIC: STUDY OF TOXIC EFFECTS OF XENOBIOTICS AND THEIR BIOTRANSFORMATION PRODUCTS
Background. The nervous system damage caused by neurotoxicants is characterized by various morphological changes, manifested mainly by dystrophic and necrotic processes. The key mechanisms of post-intoxication asthenia pathogenesis, determined by the specifics of the toxicant, involve activation of apoptosis, trophic disorder, lipid peroxidation (LPO), neuropeptide regulatory insufficiency, as well as cerebrospinal fluid dynamics disorders.
Objective. Quantification of the contribution of apoptosis, oxidative stress, and neurotrophin regulation processes to the formation of long-term health consequences of severe acute poisoning with neurotropic toxicants.
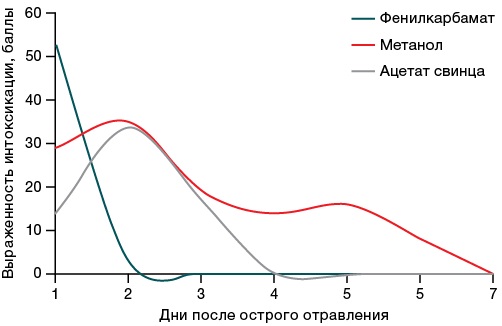
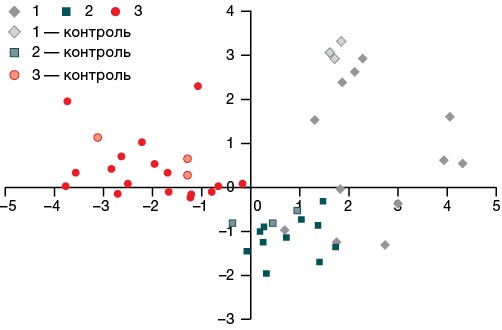
Material and methods. Experimental studies were performed in male rats. The following toxicants were used: phenylcarbamate (1.6 mg/kg bw), methanol (11.5 g/kg bw), lead acetate (300 mg/kg bw). The period of formation of long-term health effects was 30 days. The level of apoptosis of the brain temporal cortex neurons was evaluated by the TUNEL method. The identification of blood plasma neurospecific proteins was carried out by the ELISA method. Evaluation of LPO and antioxidant system was carried out by standard biochemical methods.
Results. Exposure to the substances caused the signs of toxic effects in rats on days 1–2. The maximum severity of poisoning with phenylcarbamate was on the first day, while the maximum severity of poisoning with methanol and lead acetate was manifested on the second day. By days 5–7, the survived animals showed a normalization in the status regardless of the toxicant. On day 30, violations were detected, the totality of which allowed the survived animals to be divided into subgroups according to the manifestation of functional signs of long-term health effects of acute poisoning.
Conclusions. The formation of long-term health effects of severe acute poisoning with the studied neurotoxicants was shown to be associated with an increase in the number of TUNEL positive neurons and a decrease in the S100 protein serum concentration. Lipid peroxidation in brain tissues during the specified period did not play a significant role in apoptosis activation.
Introduction. Forensic medical examinations frequently encounter poorly understood, potentially hazardous psychoactive substances. At the same time, information on the biological activity of such substances may be either fragmentary and contradictory or absent altogether. Therefore, the development of approaches to predicting the health hazard of xenobiotics is an urgent task of emergency medicine.
Objective. To study the relationship between physicochemical properties and the hazard rate of one class of CNS-active substances using the methods of mathematical analysis followed by scientific substantiation of criteria for preliminary hazard assessment of narcotic drugs.
Маterials and methods. The study models included the known structures of narcotic analgesics, divided into three groups according to their potential hazard rate. The physicochemical properties of such substances, i.e., molecular weight, polarity, polar surface area, distribution coefficients, and basic dissociation constants were considered as potential hazard factors. Linear discriminant analysis was used to identify the relationship between the physicochemical properties of psychoactive substances and their hazard potential.
Results. The considered example of one class of CNS-active substances confirms the relationship between their hazard rate and the physicochemical properties affecting their redistribution from the central bloodstream to the central nervous system. Physicochemical criteria for predicting the hazard rate of psychoactive substances are proposed. These criteria serve as classification functions that distinguish groups of model substances.
Conclusions. The physicochemical properties of psychoactive substances and the strength of their binding to target receptors equally determine the characteristics of their toxic effect. The formulated classification functions, calculated based on the physicochemical properties of substances, can be used for a preliminary hazard assessment of xenobiotics during their detection in biological samples.
Introduction. Metabolic activation of xenobiotics, including pharma drugs, is considered to be one of the main mechanisms for the development of idiosyncratic reactions. Accordingly, the potential bioactivation of a xenobiotic should be carefully evaluated in the early stages of drug development. In this regard, the search for new rapid and effective screening techniques for reactive metabolites of xenobiotics presents particular interest.
Objective. Development of a new technique for modeling the processes of xenobiotic biotransformation in vitro to identify potential metabolites of indapamide.
Materials and methods. Non-enzymatic instrumental methods, such as electrochemical oxidation (ECO) and photocatalytic oxidation (PCO) in volume, were used as comparison methods. The second phase of metabolism was modeled by incubating the oxidation products of indapamide with a trapping agent (glutathione, GSH). The oxidation products, as well as their conjugates with GSH, were then analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC–MS/MS). The developed one-pot technique for metabolism modeling is based on a UV-induced PCO of a xenobiotic in the presence of GSH on the surface of a target functionalized with titanium dioxide followed by detection of the products by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI).
Results. In use of ECO resulted in the detection of 5 metabolites and 3 adducts with GSH, while the use of PCO in the volume allowed detection of 7 metabolites and 1 adduct with GSH. The new one-pot technique detected 8 adducts with GSH. In addition to the detection of a number of known indapamide metabolites and their conjugates with GSH, a total of 4 previously unstudied metabolites and adducts with GSH were each detected for indapamide by the three methods.
Conclusions. In comparison with ECO and PCO in volume, the proposed analytical technique for modeling indapamide metabolism showed its higher informativity combined with simplicity and rapidity, which makes it a promising candidate for use in preclinical studies of drugs in predicting the metabolism and toxicity of pharmaceutical objects, as well as in studying the biotransformation processes of various xenobiotics.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Introduction. Thermal stress is an increase in body temperature due to the predominance of heat received from outside or released during metabolism over heat losses by the body. Heat production can be regulated using benzodiazepines in doses unattainable with a single intramuscular injection of their officinal preparations. In this study, this limitation is overcome using a prototype of the Phenazepam nasal spray (PNS) preparation, containing 170 mg of phenazepam in 1 mL of a non-aqueous solution.
Objective. Experimental assessment of the PNS effect on the metabolic rate and thermal balance in thermal stress.
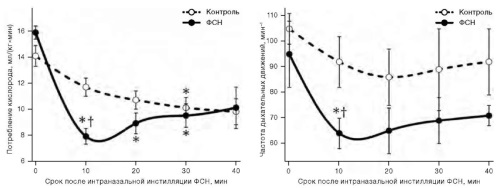
Materials and methods. The effect of a single 10 μL PNS intranasal instillation on the external respiration intensity, oxygen consumption, as well as 10 μL PNS intranasal instillations at 0.5 h intervals on the dynamics of rectal temperature, body weight, and lethality in rats at an air temperature of 40 °C was studied.
Results. PNS instillations reduced oxygen consumption by an amount sufficient to decrease body temperature by 0.3 °C in 0.5 h. PNS administration declined the rate of body temperature rise when placing rats in restrainers at an air temperature of 40 °C; however, PNS administration accelerated body temperature rise and increased lethality when placing rats in cages. Due to PNS, moisture loss by rats in cages decreased, judged by the dynamics of body weight.
Conclusions. The study confirmed the prospects of PNS as a pharmacotherapy for heat stroke at a high relative humidity, exposure to insulating skin protectors, or with immersion hyperthermia. The possibility of the aggravating effect of PNS on human thermal stress in the absence of physical obstacles to heat transfer by evaporation requires additional verification.
NEUROLOGY & PSYCHIATRY
Introduction. The etiology of multiple sclerosis (MS) remains unknown. According to the current consensus, susceptibility to MS is due to an elaborate interaction between genetic predisposition and multifactorial environmental factors, including vitamin D deficiency, smoking, inflammatory diet, psychoemotional stress, and infections. With regard to the infectious component, for decades, MS has been associated with a prior infection with the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). However, it remains unclear why only a limited proportion of the numerous EBV-infected population develop MS.
Objective. To discuss the factors of interaction between the immune system and EBV that predispose to the development of MS, as well as to analyze the possibilities of their use as therapeutic targets for the prevention and treatment of MS.
Discussion. The results of a recent large epidemiologic study have provided new evidence for the association between EBV and MS. It has also been shown that cross-reacting antibodies to myelin sheath antigens can be detected in the blood of patients with EBV. However, most patients with EBV do not develop MS. This is probably due to the elimination of autoreactive cells. Natural killer (NK) cells play a particularly important role in this process. In MS, NK-mediated elimination of autoreactive B cells may be impaired. In this regard, an add-on therapy of MS aimed at controlling EBV-induced autoimmune responses appears promising.
Conclusions. Reduced cytotoxic activity of NK cells against cells that show cross-reactivity to EBV antigens and components of the myelin sheath is among the factors of interaction of the immune system with EBV that contribute to MS development. As an add-on therapy for MS, it may be reasonable to use agents that reduce the presence of EBV in the organism and have a favorable safety profile (e.g., curcumin and quercetin). The search for agents that can improve immunological control of autoreactive cells is also promising. Such agents may include compounds that are capable of enhancing the activity of NK cells, for instance, urolithin A, curcumin, and alloferon.
Introduction. The severity of endothelial destruction in patients with the new COVID-19 new coronavirus infection may be correlated with the risk of developing acute cerebrovascular accident (ACVA).
Objective. To study the role of hemostasis system activation markers and vascular wall damage markers in the development of stroke in patients with the new coronavirus infection.
Materials and methods. The study included 38 patients with the new coronavirus infection and ACVA and 40 patients with the new coronavirus infection without ACVA. All patients were tested for antibodies to β2-glycoprotein, antibodies to cardiolipin, plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 (PAI-1), α2-antiplasmin, intercellular adhesion molecule type 1 (ICAM-1), von Willebrand factor, and homocysteine.
Results. No statistically significant differences were found between the groups in terms of antiphospholipid antibody levels; however, increased antibodies to β2-glycoprotein relative to the reference interval were more frequent in the group without ACVA. Significant differences in PAI-1 levels were found between the group with ACVA and the comparison group (p < 0.001), with the PAI-1 concentration being 1.6 times higher in the comparison group. No significant differences were observed between the groups in terms of α2-antiplasmin, ICAM-1, and von Willebrand factor levels. Significant differences for homocysteine were found between the ACVA group and the comparison group (p < 0.001), with the concentration in the comparison group being 1.8 times higher.
Conclusions. The development of acute cerebrovascular accident in patients with lower concentrations of homocysteine and PAI-1 may be explained by weaker compensatory mechanisms aimed at repairing of the vascular wall and harmonization of interaction of hemostasis system links, which eventually led to vascular wall damage.
Introduction. Schizophrenia is a complex mental disorder with heterogeneous symptoms, including psychotic, negative, cognitive, affective, and psychomotor symptoms. Although the pathogenesis of schizophrenia is mainly associated with neurotransmitter imbalance, recent studies have suggested the importance of neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis of this disease.
Objective. To study the involvement of neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia and a prognostic assessment of the potential anti-inflammatory effect of antipsychotic medications.
Discussion. Current data indicate a significant role of neuroinflammation in the development and course of schizophrenia. At the initial stages of its development, the number of lymphocytes and the level of some proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β) increase, which can be decreased by antipsychotic therapy. Studies involving experimental models of maternal immune activation (MIA) and data obtained by immunohistochemical and PET studies confirm an abnormal activation of microglia, indicating the involvement of innate immune cells. Adaptive immune response cells can also play a significant role in the development of neuroinflammation in schizophrenia. Thus, an increased level of Th17 cells and an increase in the production of proinflammatory cytokines, correlating with the disease severity, were revealed. The role of neurotransmitters in modulating the immune-inflammatory response is discussed. Available data suggest that the participation of dopamine in the schizophrenia pathogenesis can be mediated by its immunomodulatory effect. The role of neuroinflammation in schizophrenia is also indicated by the clinical effectiveness of anti-inflammatory treatment in this disease. On the other hand, the immunomodulatory effect of antipsychotics has been established, which, at least in part, may mediate their clinical effectiveness in schizophrenia.
Conclusions. Given the importance of neuroinflammation in the schizophrenia pathogenesis, further studies into both the anti-inflammatory properties of antipsychotics and the effects of anti-inflammatory drugs in schizophrenia are promising in order to further optimize the treatment of this disease.
MOLECULAR EPIDEMIOLOGY
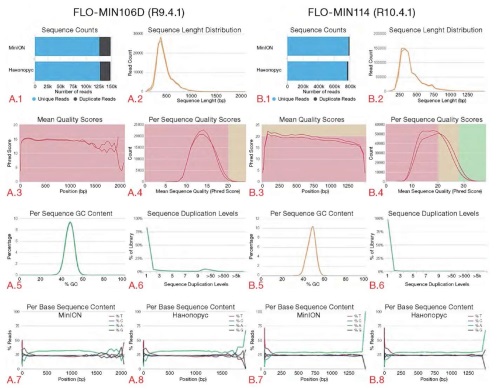
Introduction. Nanopore sequencing technologies have become routine methods in science and medicine, being widely used in the study of pathogen diversity and distribution and playing a key role in field epidemiology.
Objective. Comparative evaluation of the functional capabilities of third-generation MinION and Nanoporus sequencers in the detection of pathogens in biological material, including comparison of the as-determined taxonomic composition with the results obtained using the second-generation MiSeq (Illumina) reference platform.
Materials and methods. A total of 138 archival DNA samples with known taxonomic composition (14 families, 20 genus, and 43 species of viral and bacterial pathogens; altogether 169 pathogens) were analyzed. MinION and Nanoporus nanopore sequencers with original R9.4.1 and R10.4.1 flow cells (ONT), as well as the high-performance MiSeq (Illumina) platform were used for preliminary identification of the composition of samples containing different titers of pathogen nucleic acids belonging to various taxonomic groups. Comparative evaluation of the obtained data (number of sequences, average read quality scores (Qscore) for each nucleotide, GC-content of sequences, sequence length distribution, read duplication level) was performed using the MultiQC bioinformatics tool (version 1.20).
Results. The MinION and Nanoporus devices identified 98.8% and 97.6% of pathogens, respectively, including understudied or new viruses. The use of the latest-version flow cell on both devices significantly reduced the share of low-quality reads. The findings demonstrate a high degree of correlation between the results obtained by the second- and third-generation sequencers, which confirms the comparability and interchangeability of these technologies for the purposes of pathogen nucleic acid identification.
Conclusions. The study results demonstrate the potential of MinION and Nanoporus nanopore sequencers for epidemiologic surveillance. These devices are capable of identifying pathogens of different nature with high accuracy and, due to their compactness and portability, facilitating the diagnostics and monitoring of infectious diseases.
ОNCOLOGY
Introduction. Chronic myeloid leukemia is a myeloproliferative disease associated with a t(9;22)(q34;q11) translocation resulting in a chimeric BCR::ABL1 gene. Molecular genetic studies are used as a diagnostic method and for determination of minimal residual disease by quantification of the mRNA expression level of the chimeric BCR::ABL1 gene.
Objective. To validate the developed multiplex test system for simultaneous quantitative determination of e13a2 (b2a2) and e14a2 (b3a2) transcripts of translocation p210 in comparison with the analog system registered in Russia.
Materials and methods. In total, 50 peripheral blood samples were used. Of these, 39 belonged to patients diagnosed with CML; 11 blood samples from healthy people were used to confirm analytical specificity. The reagent kit includes the specifically developed primers and fluorescently labeled probes, the concentration of which was selected experimentally, as well as original reagents manufactured by the Centre for Strategic Planning, Federal Medical and Biological Agency (Russia). Statistical analysis was performed using the StatTech v.4.5.0 software (developed by StatTech, Russia). Differences were considered significant at p < 0.05.
Results. The conducted analytical and diagnostic characterization of the developed kit showed the following results. The relative sensitivity determined using cell standards was 0.01 %. The reproducible analytical sensitivity was 100 copies/mL (CV = 1.86 %). In analytical specificity testing, the absence of false results was shown. When testing the reagents of the test system on clinical samples, the complete convergence (100 %) with the results obtained using the reference kit was revealed.
Conclusions. Approbation of the developed reagent set showed its sufficiently high analytical sensitivity and diagnostic sensitivity. This set can be used for identification and quantitative determination of the mRNA of the chimeric BCR::ABL1 gene for the purposes of diagnosis, timely and accurate therapy, and monitoring of minimal residual disease.
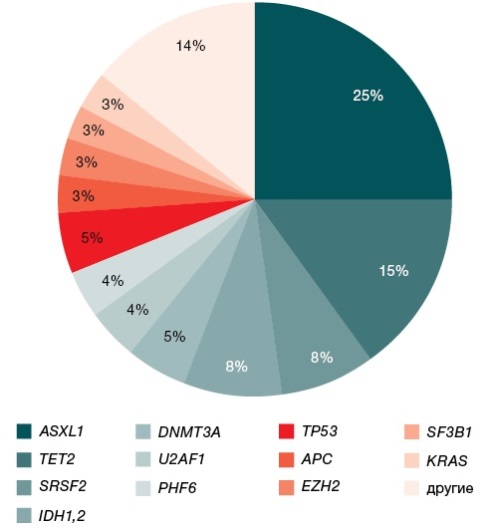
Introduction. The identification of driver mutations in the JAK2, CALR, and MPL genes is a gold standard approach in the molecular diagnosis of patients with Ph-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms (Ph-MPNs). However, such patients are characterized by a heterogenous genomic landscape. Standard molecular genetic methods cannot be used to identify most somatic mutations, thus failing to provide a comprehensive understanding of the course and prognosis of Ph-MPNs and to confirm the clonality of the disease in patients with triple-negative status. The next generation sequencing (NGS) technology allows simultaneous analysis of an extensive panel of genes and identification of both pathogenic and driver mutations.
Aim. To evaluate the possibility of using NGS to study the mutational status of patients with Ph-negative MPNs and to analyze the effect of identified pathogenic mutations on patient survival.
Materials and methods. The study included 83 patients with polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and primary myelofibrosis aged from 19 to 85 years (the median onset age of 51 years). For all patients, sequencing was performed using a myeloid panel of 118 genes with an average reading depth of 1000x on MiSeq (Illumina, USA). The clinical significance of the mutations was determined using the COSMIC and Franklin databases. The survival rate was analyzed using the Kaplan–Meyer method followed by assessment of statistical significance using the Cox-Mantel test in the GraphPad Prism 8 environment.
Results. Pathogenic mutations in 23 genes were detected in 39 (46%) patients out of the total cohort of patients. The most frequent mutations were detected in the ASXL1 gene in 25% of patients, which reduced event-free survival by 50.3% (Me = 7.83 years vs 15.75 years). The pathogenic mutations identified in other genes combined with mutations in driver genes also decreased event-free survival compared to patients with isolated driver mutations. Two or more pathogenic mutations significantly reduced event-free survival compared to patients with only one pathogenic mutation. The NGS method was also capable of identifying pathogenic mutations in 8 out of 10 triple-negative patients studied, thus confirming the clonality of the disease.
Conclusions. The next-generation sequencing (NGS) method using a panel of 118 genes is an effective tool in identifying predictively significant mutations important for selecting the most effective personalized therapy to achieve hematologic response.
REGENERATIVE MEDICINE
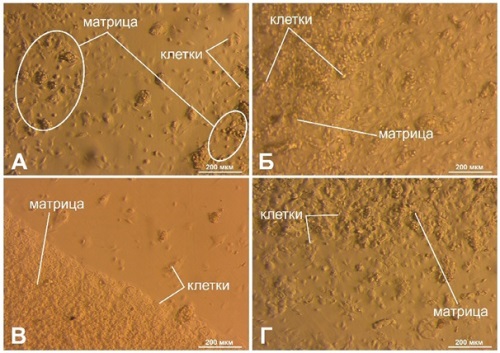
Introduction. Carriers intended for cell culture and transplantation are widely used in modern tissue engineering. The creation of inks for printing such media assumes a wide range of variations in their shape and architecture. Chitosan as a natural polymer is increasingly finding application in various fields of regenerative medicine. Chitosan-based scaffolds are an artificial prototype of the extracellular matrix in vitro. The method of 3D printing can be used to bring the structure of such a matrix as close as possible to the properties of native tissues. However, in order to achieve the desired printing quality, the task of developing a chitosan-based ink composition and selecting optimal printing parameters should be solved.
Objective. Development of a biocompatible chitosan-based ink with optimal rheological properties suitable for 3D printing.
Materials and methods. A bioink was manufactured using the chitosan produced by BiologHeppe (Germany) with a molecular weight of 164 kDa and a deacetylation degree of 92.5%. Starch produced by Merck (Germany) was used to modify the bioink. The method of 3D extrusion bioprinting was used to obtain 3D matrices by a 3D bioprinter by Rockit Invivo (Republic of Korea) equipped with the Android OS software. 3D-printed matrices were obtained from a bioink with different chitosan concentrations: 4% and 6%. Cultures of rabbit mesenchymal stem cells were seeded to study the biocompatibility of the printed structures.
Results. The developed chitosan- and starch-based inks demonstrated an increased viscosity of the solution and improved characteristics of the printed designs. The rheological parameters were optimized for printing by increasing the chitosan concentration in the solution up to 6%, as well as by introducing starch at a similar concentration into the solution. An in vitro study also showed the biocompatibility of the printed structures with respect to mesenchymal stromal cells.
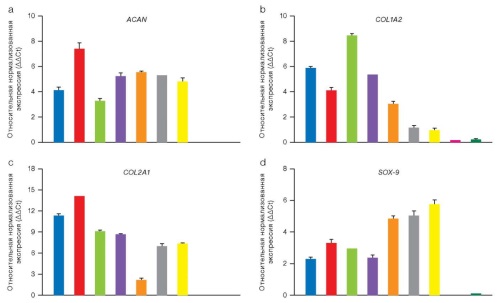
Introduction. The use of cellular constructs based on human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) is associated with a number of challenges, including the need to standardize methods for cultivating chondrocyte-like hPSCs derivatives to produce a cartilage tissue similar to natural hyaline cartilage. Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) are the basis of the extracellular matrix (ECM) of cartilage tissue; therefore, a qualitative and quantitative analysis of the GAG composition of cartilage-like tissue engineering structures is an important step in the final assessment of their potential therapeutic effectiveness.
Objective. To determine the composition of GAGs synthesized in vitro by chondrocytes of various origins using enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA) and liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS), as well as to evaluate the effect of 2D and 3D culturing on their synthesis.
Materials and methods. We analyzed the GAG levels in 2D and 3D tissue-engineered structures obtained from the cartilage tissue of five donors, chondrocyte-like cells differentiated from two hPSC lines. Cellular spheroids were obtained by aggregation in microlunar plates and cultured in mini-bioreactors. The analysis of the GAG content in cell culture samples and spheroids was carried out using ELISA and LC–MS/MS. The Kruskal–Wallis and Dunn tests were used to assess the statistical significance of the differences between the samples.
Results. The ELISA study revealed statistically significant differences (p < 0.0021), confirming higher levels of GAGs synthesized in 3D cultures of native chondrocytes compared to 2D cultures (108.67 ng/mL and 1099.87 ng/mL, respectively). The average number of spectra of the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4 protein, determined using LC–MS/MS, was also higher in 3D cultures, amounting to 41.75 spectra compared to 2.24 spectra in 2D culture samples. The levels of aggrecan, biglican, and decorin did not differ between cultures. 3D cultures of chondrocyte-like cells from hPSC showed no significant differences in the content of GAG compared to 2D cultures, which indicates the need to optimize the conditions for their differentiation.
Conclusions. In our study, the composition of the GAGs synthesized in vitro by chondrocytes of various origins was determined using ELISA and LC–MS/MS. The the effect of 2D and 3D cultivation on their synthesis was evaluated. The results showed that 3D culture media create favorable conditions for a more complete formation of chondrocytic ECM in native chondrocyte samples. Despite this, the obtained spheroids of chondrocyte-like hPSCs derivatives fail to achieve functional identity with natural cartilage tissue, even after completion of differentiation protocols, thus not representing optimal tissue engineering structures for correcting cartilage defects.
CLINICAL LABORATORY DIAGNOSTICS
Introduction. Increasing the sensitivity of immunochromatographic assay as an express method for detection and diagnosis of pathogenic microorganisms and toxins is a relevant task with regard to ensuring food safety and population health in general.
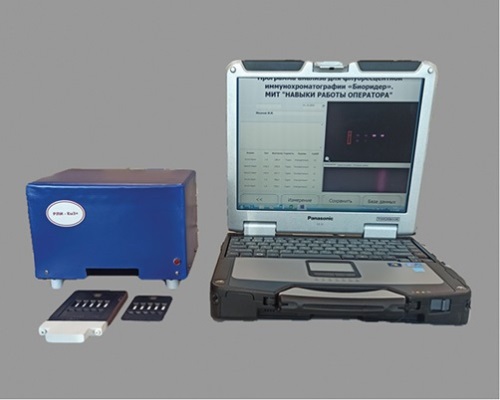
Objective. Development of a prototype of a video digital recorder of luminescent immunochromatograms (RLI-Eu³⁺) and luminescent immunochromatographic tests (LICHT) adapted to a device based on microspheres with europium compounds. Comparison of the sensitivity of LICHT and AuNPs-based immunochromatography assay (ICA) tests to increase the sensitivity of the method for detection of pathogenic microorganisms and their toxins.
Material and methods. Submicron polymer microspheres labeled with organic complexes of trivalent europium (Eu³⁺) were used as a luminescent label for immunochromatography. LICHT were recorded using the developed RLI-Eu³⁺ recorder.
Results. The detection threshold of the Eu³⁺ luminescent complex on the immunochromatographic membrane was shown to be 2 pg/mm², with the linearity of the readings ranging within 2–200 pg/mm². The coefficients of variation of the instrument readings in the luminescent complex concentration range of 20–200 pg/mm² and 2–20 pg/mm² were found to be less than 5% and 10%, respectively. Using LICHT and the RLI-Eu³⁺ device, detection thresholds were determined as follows: cholera toxin — 10 ng/mL, staphylococcal enterotoxin type B — 0.5 ng/mL, plague pathogen cells — 1×10³ cells/mL, anthrax pathogen spores — 5×10³ spores/mL, Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever (CCHF) virus antigens — at a dilution of 1:640,000.
Conclusions. The developed video digital recorder RLI-Eu³⁺ and LICHT based on europium coordination compounds enabled the detection threshold of pathogenic microorganisms and bacterial toxins to be reduced by 20–128 times compared to immunochromatographic tests based on colloidal gold (CG) for the same pathogens.
SPORTS MEDICINE
Introduction. Plantar fasciitis (PF) is a multifactorial pathology that restricts an athlete’s training and competitive activities, leading to premature termination of a sports career in some cases. The search for optimal conservative treatment methods that may improve the overall therapy effectiveness represents an important task of sports medicine.
Objective. Development of a differentiated approach to conservative treatment of athletes suffering from PF, taking the biomechanical features of the disease into account.
Materials and methods. The study involved 82 athletes, including 37 men and 45 women suffering from unilateral PF with a median age of 30 (23; 34) years. The participants were divided into four groups depending on the type of therapeutical action: Group 1 — shock wave therapy (ESWT); Group 2 — vibration therapy combined with myofascial release of the muscles of the posterior thigh and shin; Group 3 — individual orthoses of the feet; Group 4 — a combination of vibration therapy, myofascial release, individual orthoses of the feet. The tested therapeutic measures were assessed by the dynamics of pain syndrome, the results of baropodometry, the severity of tension in the thigh and shin muscles, and changes in the thickness of plantar aponeurosis.
Results. All the studied treatment methods showed varying degrees of effectiveness in reducing pain (p < 0.001), reducing the thickness of plantar aponeurosis (p < 0.05), normalizing plantar pressure in the posterior and anterior parts of the affected foot (p < 0.05), and increasing the postural stability of athletes according to objective indicators (p < 0.05). The use of ESWT resulted in the most pronounced reduction in pain. In Groups 2 (vibration therapy and myofascial release) and 3 (individual foot orthoses), a statistically significant decrease in muscle tension in the posterior shin group was observed (p < 0.05). In addition, in Group 2, the angle of dorsiflexion of the ankle joint increased significantly (p < 0.05). Group 4 (combined treatment) demonstrated the highest level of biomechanical stability.
Conclusions. ESWT demonstrates a high effectiveness in relieving a pronounced acute process. In cases where an athlete experiences some biomechanical disorders or deformities of the foot, orthoses of the feet are advisable. In case of tension of the shin muscles and limitation of dorsiflexion, vibration therapy combined with myofascial release is recommended.
SPACE MEDICINE
Introduction. Research into the microvasculature as an integral component of the cardiovascular system is particularly relevant in space medicine for identifying adaptive changes to weightlessness and developing new diagnostic criteria for assessing the functional state of an astronaut’s body in long-duration space flights.
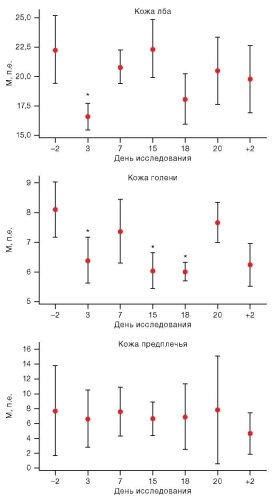
Objective. To study the process of microcirculation and its regulation in various skin areas in healthy volunteers under conditions of 21-day head-down (–6°) bed rest (HDBR).
Materials and methods. The experiment involved six male volunteers aged 26–34 years. To simulate translocation of liquid media and physical inactivity, the subjects remained in an antiorthostatic position for 21 days. Microcirculation was studied by laser Doppler flowmetry using LAZMA PF portable laser analyzers (SPE “LAZMA” Ltd, Russia). Participant examination was conducted two days prior the onset of the study, on the 3rd, 7th, 15th, 18th, and 20th day of experimental exposure, as well as two days after the completion of HDBR. Statistical data analysis was performed using the Statistica 13.0 software (IBM, USA).
Results. On day 3 of HDBR exposure, a statistically significant decrease in basal perfusion and the amplitude of myogenic oscillations in the skin of the forehead and shin was observed. The analysis of functional tests on the forearm showed a decrease in the respiratory test index by 10.87% throughout the experimental period. On day 3 of hypomobility, a decrease in the venuloarteriolar response by an average of 10.64% and an increase by 91.82% in the capillary blood flow reserve were noted, with the latter persisting throughout the entire exposure.
Conclusions. The effect of HDBR is expressed in a decrease in skin perfusion against the background of increased tone of terminal arterioles and precapillary sphincters in the forehead and lower legs, which may indicate microcirculation shift toward larger vessels. Despite the skin perfusion stability in the forearm area at rest, the conducted functional tests showed the probability of changes in vasomotor function under the action of HDBR.
SURGERY
Introduction. Recent progress in abdominal surgery and operative gynecology has led to a significant increase in the number of patients with postoperative abdominal adhesions. The incidence of adhesions after abdominal surgery reaches 67–95%, a serious health problem. In their presence, any following operations may be associated with an increased risk of intra- and postoperative complications.
Objective. To study the possibility of laparoscopic access and its outcome in the surgical treatment of women with reproductive system diseases concomitant with pronounced abdominal and pelvic adhesions.
Materials and methods. A retrospective analysis of 265 patient medical records was performed. The general group included 91 women who had undergone surgery for diseases of the reproductive system in the setting of pronounced abdominal and pelvic adhesions. The second group (control) comprised 174 patients who had undergone surgery for diseases of the reproductive system and had no adhesions. The average age of the patients in the general and control groups was 47.1 ± 12.8 and 46.5 ± 8.1 years, respectively. The preoperative examination included ultrasonography and dynamic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the abdominal cavity and lesser pelvis. For laparoscopic surgery, a STORZ high-resolution video system (Germany) and a BOWA power plant (Germany), including high-frequency (HF) electric, laser, and argon plasma energy, were used. Statistical data processing was carried out using the Statistica 13 and MS Office Excel software. The result was considered statistically significant at p < 0.05.
Results. The conducted comparative analysis demonstrated the possibility of using laparoscopic access for the treatment of women with reproductive system pathologies in combination with pronounced abdominal and pelvic adhesions. The duration of surgery, the volume of blood loss, the severity of pain, the duration of hospitalization, and convalescence had no statistically significant differences between the general (n = 91) and control groups (n = 174). The absence of differences in the frequency of intra- and postoperative complications proves laparoscopic access to be safe in the setting of severe adhesions. The safety is ensured by preoperative patient preparation and examination, use of necessary modern equipment and tools, surgical skills and experience.
Conclusions. The use of laparoscopic access for performing surgical treatment of patients with reproductive system diseases in combination with pronounced adhesions can be considered as the preferred and safe treatment method.
ISSN 2713-2765 (Online)