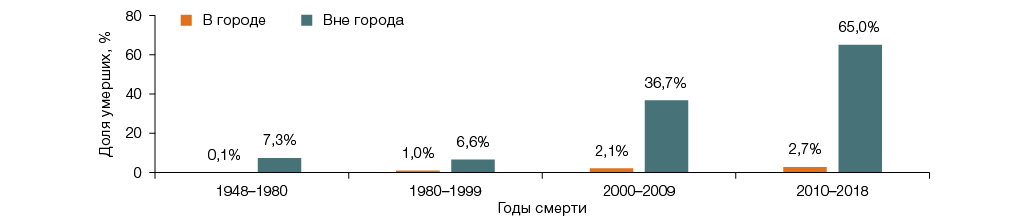MAIN TOPIC: CURRENT ISSUES IN TOXICOLOGY
Introduction. The determination of metabolism and pharmacokinetics is an essential requirement in the development of any drug. Phaeosphaeride A (PPA) is an anticancer agent belonging to the group of natural compounds with antitumor properties, which was first isolated from the endophytic fungus FA39 by Harvard scientists (Claudy et al.) in 2006. In this study, we investigate compound AV6, which is a derivative of natural phaeosphaeride A.
Objective. To study the acute toxicity and pharmacokinetic characteristics of the semi-synthetic substance AV6 obtained based on phaeosphaeride A, a natural phytotoxin with antitumor properties, following a single intragastric administration of AV6 in laboratory rodents.
Materials and methods. The acute toxicity of AV6 was studied using 30 male Balb/c mice, which were divided into five groups of six animals each. The control group received a single intragastric administration of a solvent (oil-alcohol emulsion, 300 µL volume), while four experimental groups received AV6 at doses of 5, 50, 300, and 2000 mg/kg bw. Body weight dynamics were evaluated, and organ mass coefficients were calculated. The pharmacokinetic study was performed following a single intragastric administration of AV6 at a dose of 25 mg/kg bw to outbred male Wistar rats. The AV6 dose for the pharmacokinetic study was determined based on acute toxicity data, accounting for the interspecies conversion factor. Quantitative determination of AV6 in blood plasma and urine was performed using the MS/MS method. Statistical analysis was conducted using GraphPad Prism 5 software.
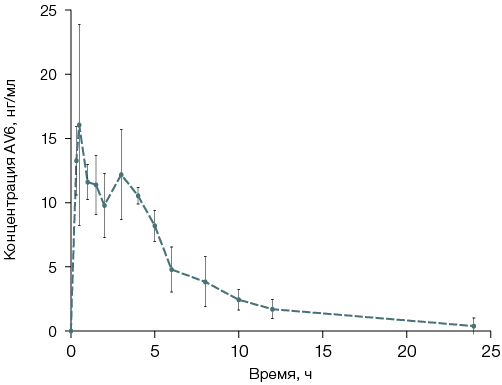
Results. According to the acute toxicity data following intragastric administration, the AV6 phaeosphaeride A derivative can be classified as hazard class 3 (animal mortality was observed exclusively in the 2000 mg/kg bw group). Visual examination of internal organs revealed no apparent macroscopic signs of pathology. No statistically significant changes in the mass coefficients of internal organs were detected in experimental animals compared to controls. A quantitative determination procedure for AV6 was developed based on HPLC–MS/MS analysis. Metabolites formed in rats in vivo were identified. A comparison of rat blood plasma chromatograms 1 h and 10 h after intragastric AV6 administration showed that, after 1 h, the AV6 peak intensity was 20 times higher than the M2 peak. However, after 10 h, the AV6 peak intensity decreased, while the metabolite M2 peak intensity increased.
Conclusion. Compound AV6 is classified as a moderately hazardous substance. Data on the structure of AV6 metabolites (a derivative of natural phaeosphaeride A) obtained during pharmacokinetic studies in rats indicate a relatively low metabolic rate of the compound. This is primarily due to chemical transformations at the nitrogen atom of the lactam ring, resulting in metabolites that may be excreted in urine. The most probable mechanisms of these transformations are oxidative deacylation followed by hydrolysis. The completed preclinical study evaluating the acute toxicity, metabolism, and pharmacokinetics of AV6 represents a crucial step in translating previous findings on the antitumor potential of this derivative of natural phaeosphaeride A and advancing in vivo research.
Introduction. Cholinesterase inhibitors present in household chemicals, agrochemicals, and a number of medicinal products represent the most common cause of acute intoxications accompanied by the development of convulsive syndrome. Delayed and repeated administration of existing antidotes proves ineffective. Compounds that are promising for the development of alternative therapeutic agents include derivatives of valproic acid.
Objective. Evaluation of the anticonvulsant efficacy of original valproic acid aminoethers in intoxication with phenylcarbamate as a cholinesterase inhibitor.
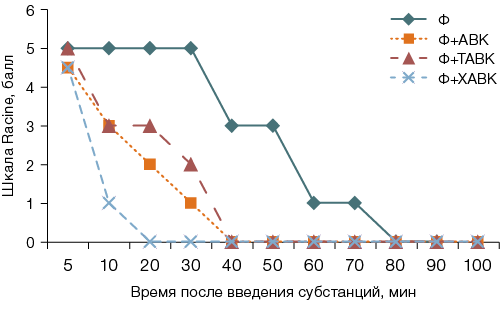
Materials and methods. Experiments were conducted using outbred white male rats aged 3 months with a body weight of 200–240 g. The tabular express method by Prozorovsky was used to determine the median lethal doses of the new compounds. To model the convulsive syndrome, phenylcarbamate was administered intraperitoneally to male rats at a dose of 1 mg/kg bw. The anticonvulsant activity of valproic acid aminoethers — N-methyl-4-piperidinol (VAA), quinuclidinol (QVA), and tropinol (TVA) — was assessed. The preparations were administered at doses of 21.5 mg/kg bw and 43 mg/kg bw after the onset of convulsions. The study was conducted using four experimental groups: phenylcarbamate — P (n = 8), P+VAA (n = 16), P+TVA (n = 16), and P+QVA (n = 16). The test substances were dissolved in 0.9% sodium chloride solution and administered intraperitoneally, taking interspecies dose conversion into account. The volume of the intraperitoneally administered solution was 0.1 mL/100 g. The severity of the convulsive syndrome in the experiment was assessed using the Racine scale. The following efficacy indicators were taken into account: latent period, severity and duration of convulsive syndrome, and mortality. Statistical processing of the research results was performed using the Statistica 13.0 software package (Statsoft, USA).
Results. The established LD50 values of the original valproic acid aminoethers under study correspond to class 3 of moderately toxic substances. At a dose of 21.5 mg/kg bw, the proportion of rats with severe convulsions significantly decreased in all groups; the fastest anticonvulsant effect was recorded in the QVA group (after 10 min, convulsions were absent). The efficacy of VAA and TVA at a dose of 43 mg/kg bw was comparable to the dose of 21.5 mg/kg bw; in the QVA group, the proportion of animals with convulsions remained high after 10 min. A significant reduction in the duration of convulsions was revealed in the QVA group at doses of 21.5 mg/kg bw and 43 mg/kg bw. A significant decrease in the intensity of convulsions was detected in the VAA and QVA groups at a dose of 21.5 mg/kg bw, and at a dose of 43 mg/kg bw in the VAA and TVA groups.
Conclusions. The new aminoethers of valproic acid exhibit anticonvulsant activity in intoxication with a reversible cholinesterase inhibitor. At a dose of 21.5 mg/kg bw, QVA is the most effective; however, at a dose of 43 mg/kg bw, manifestations of toxicity are observed and VAA is more effective. Despite animal mortality, TVA also demonstrates its efficacy at a dose of 43 mg/kg bw.
Introduction. Issues related to the epidemiologic aspects and clinical manifestations of poisoning by neurotoxicants, whose effects cause serious harm to the health of victims, are highly relevant. Acute and chronic poisoning can be manifested through diverse patterns; however, regardless of the type of neurotoxicant, all victims experience asthenovegetative and psychoorganic syndromes. These syndromes can develop during both toxicogenic and somatogenic phases of poisoning, manifesting in the period of its long-term consequences.
Objective. Scientific substantiation of the risks of poisoning by neurotoxicants, which pose a serious threat to public health due to their systemic toxic effects and the development of multiorgan pathology, including at the stage of long-term consequences of poisoning.
Discussion. In Russia, among various types of acute poisoning, intoxications by substances causing primary damage to the central nervous system rank first. The routes of entry of neurotoxicants into the body are indicated, and the forms of manifestation of neurotoxic processes are described. The pathogenesis of the toxic action of organic solvents, heavy metal salts, barbiturates, and carbamates is analyzed. Toxic neurotropic substances can adversely affect the nervous system both directly and indirectly, through damage to other organs and systems. Clinical cases of acute poisoning by neurotoxicants are described. After poisoning by representatives of the group of neurotropic toxicants, after a certain period of time, the victim develops long-term consequences with a highly varying clinical picture.
Conclusions. The presented data on poisoning exposures to neurotoxicants demonstrate the clinical and pathogenetic significance of their effects not only on the central nervous system but also on other organs and tissues, the development of systemic pathological processes and multiorgan pathologies. The identified features of the toxic action must be taken into account when analyzing the health risks to victims of poisoning with neurotropic toxicants. The most significant manifestations of the effects on other organs/tissues should be reflected in the protocols for diagnosing the severity of such poisoning accidents and their long-term consequences, as well as in the use of metabolic and cytoprotective agents for their treatment.
Introduction. The toxicity of a number of xenobiotics increases with air temperature. However, it remains unknown whether this applies to narcotic analgesics and whether this dependence can be corrected by first aid measures recommended for heat stroke.
Objective. Evaluation of the effect of elevated air temperatures and local cooling on the acute toxicity of fentanyl.
Materials and methods. Three series of experiments were conducted. In the first series, the effect of elevated air temperatures on the dose dependence of the lethal and narcotic effects of fentanyl was studied. In total, 11 groups of 20 rats each were formed, which were intravenously administered fentanyl at doses of 50, 100, 200, 300, or 400 µg/kg, and one group (n = 14) without drug administration. Following fentanyl administration, one subset of rats (n = 100) was kept for 24 h at an air temperature of 22 °C; the second subset (n = 100) was kept for 40 min in a thermal chamber at 40 °C and then for 24 h at 22 °C. Those not receiving fentanyl were observed in a thermal chamber until the first case of death, then for 24 h at 22 °С. In the second series of experiments, the effect of head cooling on lethality, latent awakening time, and rectal temperature of rats (n = 49) 40 min after intravenous administration of fentanyl at a dose of 300 µg/kg (LD5) was studied. Four groups of animals were formed, which were kept after fentanyl administration for 40 min at 22 or 40 °С with or without local cooling of the neurocranium, followed by observation for 24 h at 22 °С. In the third series of experiments, following the same scheme, the effect of cooling the middle third of the ventral surface of the torso on lethality, latent awakening time, and rectal temperature of rats (n = 48) 40 min after fentanyl administration at the same dose was studied. Statistical analysis was performed using the OriginPro software.
Results. A 40-min exposure at 40 °С was non-lethal for intact rats. After administration of fentanyl at doses of 100–400 µg/kg, lethality reached 0–5% and 60–95% at 22 °С and 40 °С, respectively. Hyperthermia induced by 40 °С exposure under fentanyl administration at a dose of 300 µg/kg was mitigated by head cooling and prevented by cooling the ventral surface of the torso. Cooling the ventral surface of the torso, rather than the head, reduced lethality from 100% to 8%. At 22 °С, both local cooling methods deepened fentanyl-induced hypothermia without significantly affecting lethality or anesthesia duration.
Conclusions. The general overheating potentiates the lethal and narcotic effects of fentanyl in rats. Under these conditions, cooling the ventral surface of the torso is an effective measure to prevent hyperthermia and lethality, while head cooling is ineffective. At room temperature, both local cooling methods deepen fentanyl-induced hypothermia without significantly affecting lethality. The efficacy of cooling the ventral surface of the torso requires evaluation not only during combined overheating but also during isolated overheating of the organism.
EMERGENCY RESPONSE ORGANIZATION
Introduction. Modern challenges to the national security of Russia necessitate improvements in the medical and sanitary support system, including the medical personnel and resources of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency (FMBA) of Russia during emergency situations, terrorist attacks, and armed conflicts. Special emphasis is placed on enhancing the promptness, effectiveness, and organization of providing specialized medical assistance and carrying out medical evacuations for victims, injured persons, and patients. This need is underscored by the existing experience of Joint Medical Teams (JMTs) of the FMBA of Russia participating in the elimination of large-scale emergency consequences and ongoing Special Military Operation (SMO).
Objective. Development of proposals for improving the regulatory framework and methodological support for the creation, preparation, use, and operation of FMBA JMTs.
Materials and methods. The study utilized normative and methodological documents of the Agency, reports from district medical centers (DMCs), and data from a survey questionnaire involving 192 medical specialists engaged in the activities of JMTs over the period from February 2022 to June 2025, including their involvement in the SMO. The following methods were employed in conducting this research: formal legal analysis, content analysis, expert evaluation, statistical processing of data, as well as logical and information modeling techniques. The study encompassed legal, organizational, and methodological aspects related to the functioning of JMTs in various types of emergency situations. The analysis took into account extensive experience in mitigating health-related consequences of emergencies and the role of such teams in facilitating medical evacuation, delivering medical aid to affected individuals, wounded soldiers, and ill servicemen.
Results. Gaps in the normative and methodological support for the activities of FMBA JMTs were established, despite their relatively high response efficiency and functional effectiveness, confirmed by their participation in providing medical support during the SMO. The expert assessments among 192 medical professionals, most of whom (60.4%) had practical experience of working within JMTs, showed dissatisfaction with the current normative and methodological basis. According to the experts, the current framework does not provide for sufficient clarity or regulation for establishing, preparing, utilizing, maintaining, and implementing medical evacuation processes by JMTs. The collected data indicate a pressing need for a comprehensive improvement of the legal and methodological basis for JMT activities. These improvements include drafting and adopting a single Standardized Regulation for JMTs, supplementing FMBA Order No. 126 dated 25.04.2022, taking into account specific tasks related to medical evacuation, entrusting DMCs with responsibilities for forming, training, and managing JMTs, and elaborating detailed methodological recommendations aimed at standardizing the organizational structure, equipping standards, and preparedness criteria for JMTs. The results obtained form a basis for resolving numerous problematic issues impeding effective functioning of JMTs.
Conclusions. The results obtained indicate gaps in the normative and methodological framework regulating the activities of FMBA JMTs, which hinder the development of clear mechanisms for their formation, application, and functioning when organizing and providing medical assistance to victims of emergencies, terrorist acts, and military conflicts. Implementation of the proposed measures will enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of JMTs within the healthcare system, contributing significantly to national security interests.
Introduction. Traumatic liver injuries are a significant challenge in modern emergency surgery. Developing new methods for surgical hemostasis of traumatic liver injuries is an extremely relevant task in urgent surgery.
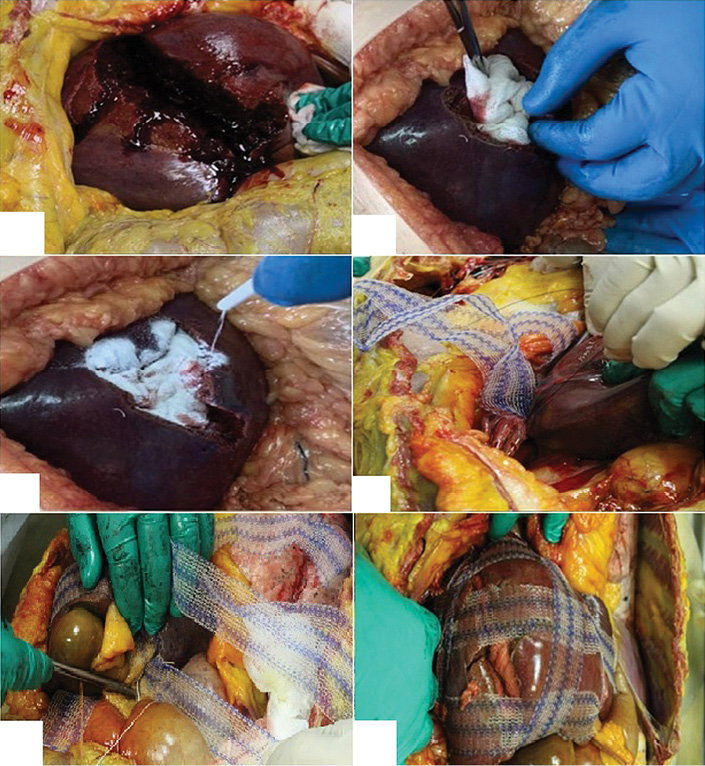
Objective. Development and testing of surgical hemostasis for traumatic liver injuries using a modified packing technique.
Materials and methods. A new method of surgical hemostasis for traumatic liver injuries was developed using cadaveric material. The clinical trial included 27 patients with severe traumatic liver injuries (AAST Grade IV). Patients were divided into the main (n = 14) and control (n = 13) groups. Patients in the main group were treated using a new method of surgical hemostasis for traumatic liver injuries, involving tamponade of the liver wounds with Surgitamp hemostatic gauze impregnated with Molselect G-50 granular sorbent, followed by modified liver packing with strips of polypropylene mesh implant. In the control group, surgical hemostasis was performed by tamponading the liver wound with hemostatic sponges followed by suturing. The effectiveness of the proposed method was evaluated based on the following parameters: definitive hemostasis, number of recurrent hemorrhages, number of reсurrent operations, mortality, hospital stay duration, intensive care unit stay duration. Statistical analysis of the study results was performed using the Statistica 10 software.
Results. The application of modified packing in the combination treatment of patients with severe traumatic liver injuries increased the reliability of definitive hemostasis from 46.2% to 92.8% (p = 0.0391), reduced the number of re-bleeding episodes and re-operations from 38.4% to 7.1% (p = 0.0391), and decreased the mortality rate from 38.4% to 14.2% (p > 0.05).
Conclusions. The application of the new combined method of surgical hemostasis improved the treatment outcomes for patients with severe traumatic liver injuries by increasing the reliability of definitive hemostasis, reducing re-bleeding and re-operations, and lowering mortality.
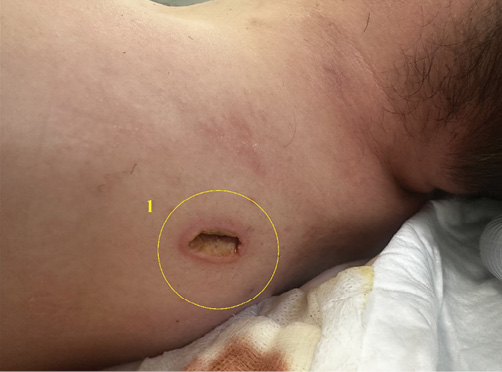
Introduction. Fragment wounds of the neck with neurovascular bundle injury sustained during combat operations represent a relevant problem in the field of extreme medicine. High mortality rates, along with a lack of sufficient research, contribute to uncertainty in determining optimal treatment tactics.
Case report. A successful surgical treatment of a serviceman with a fragment wound to the neck caused by a foreign metallic body (shell fragment) involving the internal jugular vein and a floating thrombus was performed in a field hospital. An open surgery was conducted to remove the foreign metallic body and the floating thrombus from the internal jugular vein, followed by repair of the venous wall with a 7/0 polypropylene suture. The postoperative course was uneventful.
Conclusions. The presented case demonstrates previously unpublished data on a variant of fragment injury to the internal jugular vein. The proposed surgical technique has proven to be effective and safe.
RADIOBIOLOGY
Introduction. The medical registry of workers at the Mayak Production Association (PA) was initially established with the purpose of studying the long-term stochastic health effects of occupational radiation exposure at the first nuclear industry enterprise in the USSR.
Objective. Assessment of radiogenic risk from prolonged occupational exposure among the Mayak PA worker cohort, including the subcohort of workers exposed to normal radiation conditions.
Materials and methods. This study represents one phase of a lifelong retrospective epidemiological investigation of health indicators, including the incidence and mortality from malignant neoplasms (MN), conducted within the framework of the medical-dosimetric registry of Mayak PA workers. The available study cohort is limited to employees of three main production facilities and two auxiliary plants, hired between 1948 and 1982. Within the study cohort, two subcohorts are distinguished based on factual data on radiation exposure levels and assessed medical outcomes. These include the subcohort of 1948–1958, personnel hired during the technology development phase and characterized by high occupational radiation exposure levels and that of 1959–1982, hired during routine operational periods with radiation doses comparable to modern limits. At the current stage, the attained age of workers in the second subcohort and the volume of accumulated data have enabled an analysis focused on individuals having worked under standard conditions, excluding the effects of high doses and dose rates. This has expanded the scope of statistically significant direct estimates of radiogenic MN risk. All studies of radiogenic risk in the cohort of Mayak PA workers were conducted using the Epicure statistical software package.
Results. The cohort comprised 25,755 workers. The vital status during the period of up to 31.12.2018 was known for 94% of subjects. In the 1948–1958 subcohort, the mean cumulative gamma radiation dose was 748 mGy, compared to 130 mGy in the 1959–1982 subcohort. Overall, 10,304 individuals (40.1% of the cohort) received low doses of gamma radiation. The mean cumulative lung dose from alpha radiation due to incorporated 239Pu was 179.4 mGy, with 329.2 mGy and 41.0 mGy for the 1948–1958 and 1959–1982 subcohorts, respectively. The estimated excess relative risk per 1 Gy of alpha radiation lung dose was 3.5–8 for 60-year-old males. No deviations from linearity were found. Radiogenic risk decreased with an increase in age. A nonlinear dose-response relationship was identified for liver MN. The primary long-term effect of external gamma radiation was leukemia development, where a nonlinear model incorporating effect modification by age at exposure, time since exposure, and attained age provided better approximation than a linear model. For solid MN, the risk coefficient from external gamma radiation ranged 0.1–0.4 per 1 Gy. Among workers employed under normal radiation conditions (1959–1982 hiring period), the attributable risk assessment suggests that 1–5% of MN (excluding tumors in plutonium primary deposition organs) were radiation-induced, solely due to external gamma exposure.
Conclusions. The Mayak PA worker cohort, with its high-quality medical and dosimetric data, serves as a crucial source for direct epidemiological assessments of radiogenic risks from prolonged occupational radiation exposure. The identification of the routine production operation period not only validates the magnitude of carcinogenic risk but also highlights the need to extend both the follow-up period and the cohort itself to include more workers exposed to conditions comparable to modern standards.
Introduction. The diversity of clinical manifestations of radiation sickness creates significant difficulties in the development of a versatile means for the prevention and treatment of radiation injuries.
Objective. Assessment of the prospects for using alpha-2-macroglobulin (α2M) as a radioprotective agent.
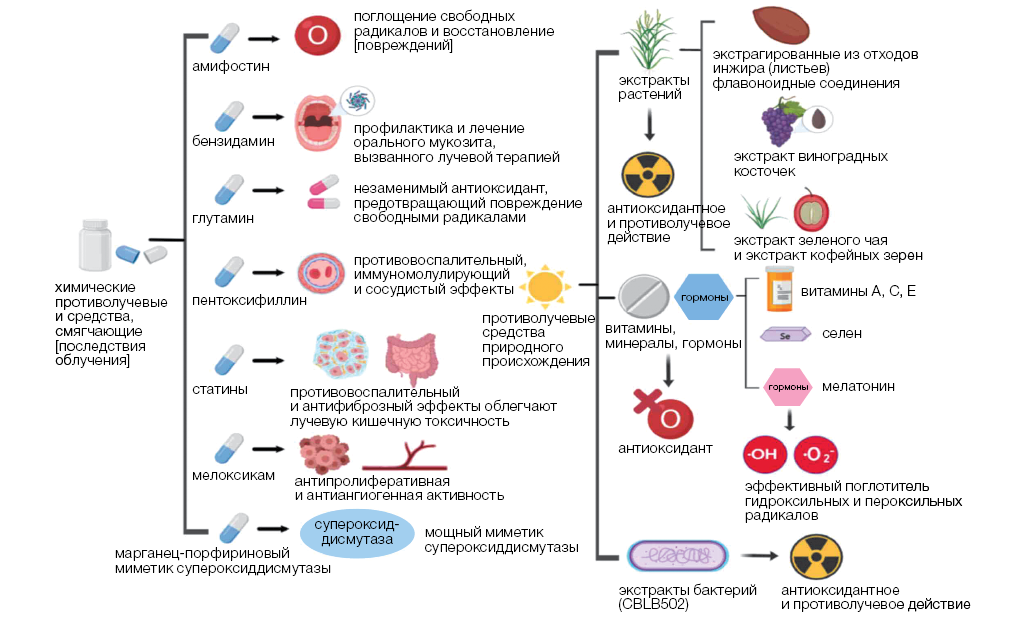
Discussion. The existing agents were established to be incapable of simultaneous implementation of multiple mechanisms of radioprotective action, rendering the development of complex formulations the primary research direction. However, the toxicity, side effects, and multidirectional nature of many radioprotectors hinders their combined application. Along with inhibiting proteinases, alpha-2-macroglobulin (α2M) is involved in lipid metabolism and regulation of the antioxidant system. It influences enzyme activity, binds and transports numerous cytokines, affects the functions of immunocompetent cells, and controls the development of the inflammatory response and tissue remodeling processes. A number of published studies confirm α2M to be a promising radioprotector and a key component of innate radioprotection.
Conclusions. Preparations based on human blood polyfunctional proteins can serve as a basis for the development of means for preventing and treating radiation injuries. The α2M administration into the body reduces lethality, protects DNA from damage, lowers the oxidative stress level, mitigates the severity of leukopenia and thrombocytopenia, and reduces the number of necrosis foci. Further research into the radioprotective properties of this protein and the optimization of methods for its isolation from blood for industrial-scale production are required.
INNOVATIVE THERAPIES
Introduction. Primary hyperoxaluria type 1 (PH1) is an inherited disorder characterized by excessive oxalate production in the liver, leading to hyperoxaluria, kidney stone formation, nephrocalcinosis, and progressive kidney damage. PH1 is caused by mutations in the AGXT gene, whereas types 2 and 3 are associated with mutations in GRHPR and HOGA1, respectively. Lumasiran, an RNA interference (RNAi)-based therapeutic agent, targets the HAO1 gene (hydroxyacid oxidase 1), thus reducing the levels of glycolate oxidase. This action results in decreased hepatic oxalate production.
Objective. Evaluation of the efficacy, safety, and clinical use of lumasiran in adults and children with genetically confirmed primary hyperoxaluria type 1.
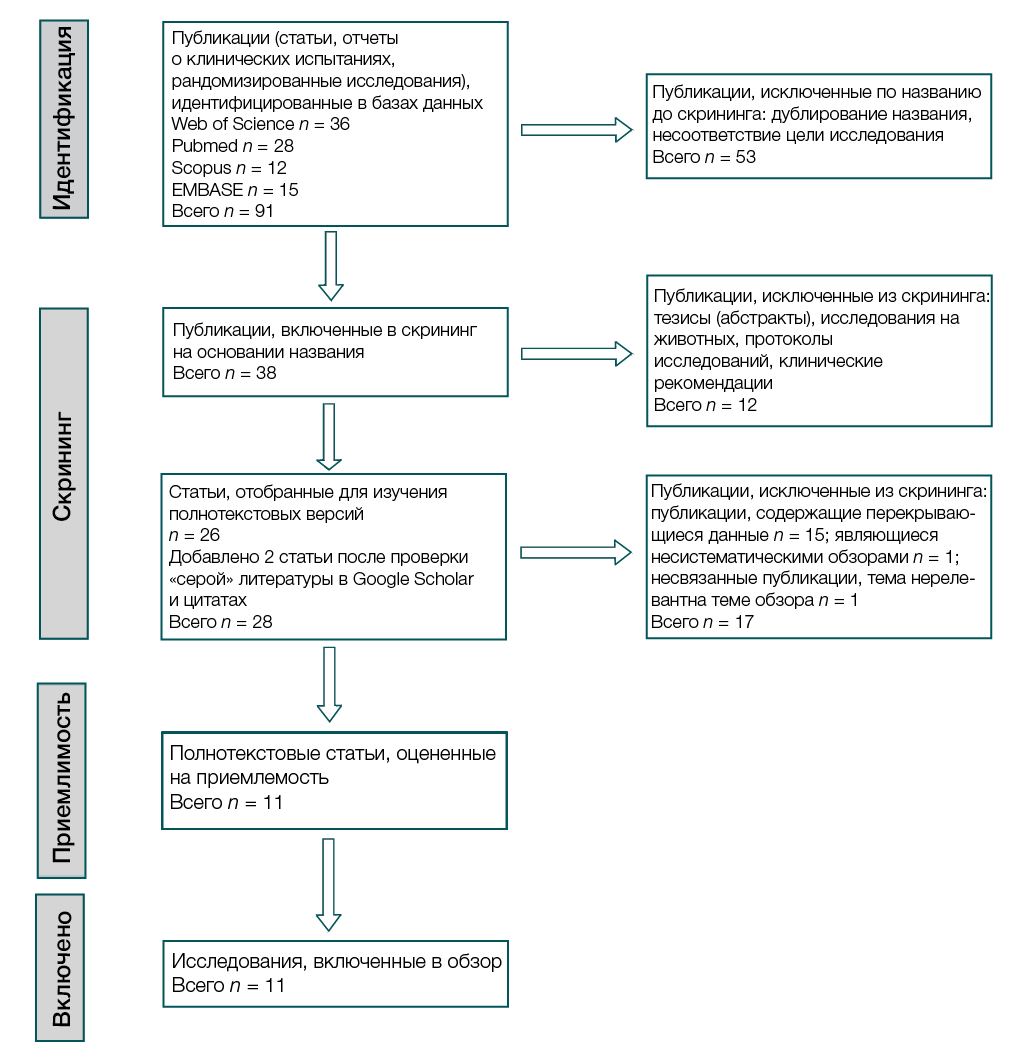
Materials and methods. The systematic review was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA 2020 guidelines. A comprehensive literature search was performed across four databases (PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and EMBASE). Studies were selected based on their focus on the use of lumasiran in pediatric or adult patients with genetically confirmed primary hyperoxaluria type 1. The quality and risk of bias were assessed using the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) critical appraisal tools. The final analysis included 11 studies: two randomized controlled trials, two prospective single-arm studies, one case series (involving five patients), and six individual clinical case reports involving both pediatric and adult populations.
Discussion. Lumasiran treatment was found to lead to a significant reduction in urinary oxalate (UOx) levels (approximately 60–75%) and plasma oxalate (POx) levels (approximately 30–60%). Patients across all age groups, from infants to adults, exhibited markedly stabilized or improved renal function, alongside reduced progression of nephrocalcinosis. Lumasiran demonstrated a favorable safety profile, with the most common adverse events being mild injection-site reactions. No serious treatment-related adverse events requiring discontinuation of therapy were reported.
Conclusions. By suppressing glycolate oxidase expression, lumasiran has consistently demonstrated significant efficacy in reducing oxalate levels. However, there exist differences in therapeutic approaches for adult patients and infants, as well as in treatment effects based on baseline renal function and dosing regimens. Both pediatric and adult populations showed substantial improvement and stabilization of renal function, although infants and patients with advanced chronic kidney disease required dose adjustments. Studies also revealed a greater variability in renal outcomes, particularly regarding the progression of nephrocalcinosis. Although additional large-scale long-term studies are needed, our findings indicate that lumasiran may impede the progression of kidney disease and potentially reduce or delay the need for kidney transplantation in PH1.
SPORTS MEDICINE
Introduction. Fractures, particularly low-energy ones, are more common in female athletes with oligo/amenorrhea compared to their peers without menstrual disorders. This problem is associated with various hormonal changes and impaired bone remodeling processes.
Objective. Assessment of bone metabolism and serum hormonal parameters in highly qualified under-18 female athletes both with primary amenorrhea and without menstrual cycle disorders.
Materials and methods. A single-center single-stage study involved 111 young female athletes aged 15–18 years (median age 15.9 [14.9; 16.6] years), who were members of Russian national teams in five sports. All the participants underwent comprehensive medical examination at the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center for Children and Adolescents of FMBA of Russia between March 2021 and July 2023. The athletes were divided into two groups based on the presence of primary amenorrhea. The group with primary amenorrhea included 23 athletes (median age 15.8 [15.1; 16.3] years); the comparison group consisted of 88 athletes (median age 15.9 [14.9; 16.6] years) with a regular menstrual cycle. Serum levels of osteocalcin, C-terminal telopeptide (β-CrossLaps), type 1 procollagen (P1NP), parathyroid hormone (PTH), vitamin D (25(OH)D3), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity were measured. To assess hormonal status, levels of luteinizing hormone (LH), folliclestimulating hormone (FSH), estradiol, and leptin were evaluated. Sexual maturity was assessed according to the Tanner rating, and body composition was evaluated using bioelectrical impedance analysis. Statistical data processing was performed using the Statistica v. 10.0 software package (StatSoft Inc., USA).
Results. Athletes with primary amenorrhea were characterized by lower body weight (p < 0.0001) and body fat percentage (p < 0.0001) compared to their peers without menstrual disorders. The analysis of LH (p = 0.328) and FSH (p = 0.069) levels did not reveal statistically significant differences between the study groups; however, the adolescent athletes with primary amenorrhea had lower levels of estradiol 182.0 [123.0; 227.0] and 244.0 [143.5; 518.5] (p = 0.002) and leptin 2.1 [1.2; 4.1] and 9.1 [5.1; 14.9] (p < 0.0001) compared those without menstrual cycle disorders. The athletes with primary amenorrhea showed an increase in both bone formation markers (P1NP, osteocalcin) and bone resorption markers (β-CrossLaps and ALP) compared to their peers without menstrual disorders.
Conclusions. Minors with primary amenorrhea are characterized by disharmonious physical development due to underweight, accompanied by reduced body fat content, decreased levels of leptin and estradiol, preserved gonadostat function, and increased markers of bone metabolism. The identified hormonal and metabolic features may represent a significant risk for impaired bone remodeling in this group of athletes.
Introduction. Approximately 46% of large joint injuries involve damage to the knee joint, among which anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries account for about 15–24% in children and adolescents. In order to reduce the likelihood of long-term complications after injuries in underage professional athletes, shorten the rehabilitation period, and enable a quicker return to elite sports, innovative regenerative medicine technologies should be implemented into clinical practice, including the use of platelet-rich plasma (PRP). In comparison with other conservative treatment methods, PRP offers several advantages. Being an orthobiological agent, PRP is a biological substance derived from the patient’s own body, promoting accelerated regeneration with minimal risk of side effects. When performed correctly, this procedure shows minimal invasiveness and does not lead to complications. Although PRP therapy is widely used in treating diseases and injuries of large joints in adult patients, the application of this therapeutic method in underage athletes has not been sufficiently studied, which is the focus of this study.
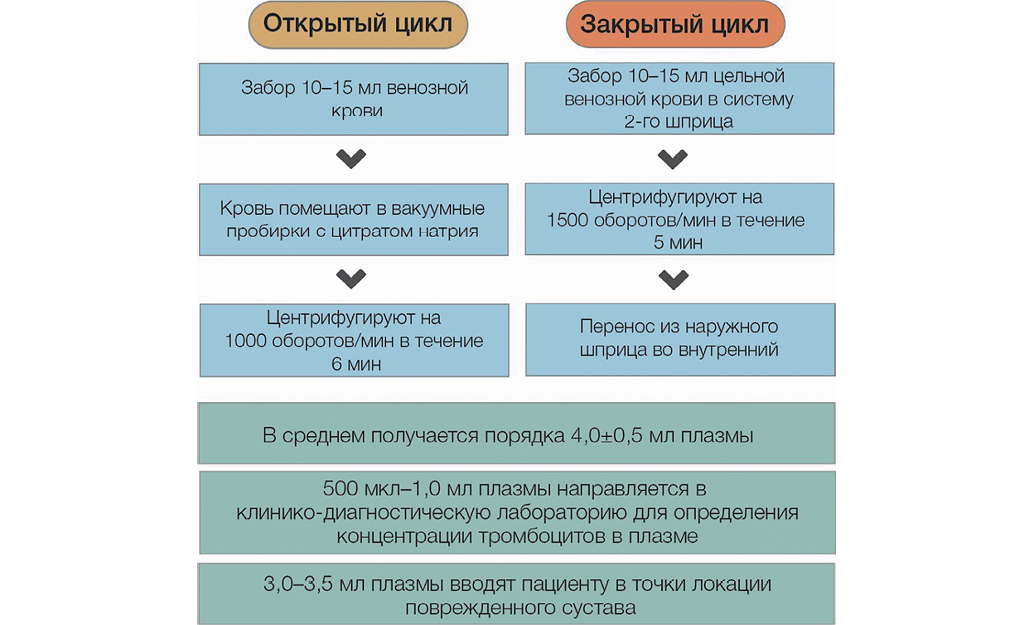
Case report. We present a clinical case of a professional athlete with a knee joint injury, assessing the functional and clinical outcomes of PRP therapy. Two standardized methods for PRP application are demonstrated, highlighting the advantages of a closed-loop PRP preparation system. These include minimized exposure to the external environment, mitigating potential risks of infection, and reduced consumption of materials, enhancing cost-effectiveness. The described clinical case of an ACL injury in a junior athlete, with complete functional and structural recovery (as confirmed by magnetic resonance imaging, MRI), demonstrated the efficacy, safety, and good tolerability of PRP therapy. Positive outcomes were observed both clinically (regression of pain assessed via the visual analog scale, restoration of joint function, and positive dynamics in provocative tests such as the Lachman test and anterior drawer test) and through MRI data.
Conclusions. The use of PRP therapy for ACL injuries in underage professional athletes represents a promising therapeutic approach in orthopedics and sports medicine, utilizing regenerative medicine technologies. The closed-loop system for PRP preparation offers several advantages over open-loop systems, including cost-effectiveness due to minimized consumption of medical supplies. The safety of the method is ensured provided that the procedural requirements are met (asepsis, antisepsis, ultrasound guidance, etc.); the high sensitivity of MRI in tracking the dynamics of ACL injuries is confirmed.
Introduction. Oral health issues, such as dental caries, periodontal diseases, or malocclusion, can cause pain, discomfort, and systemic health problems, which in turn may negatively affect the performance and endurance of athletes. In this context, the development of comprehensive dental programs for athletes involved in professional sports is a relevant task.
Objective. To determine statistically significant differences in performance parameters among combat sports athletes for the development of measures to correct the dental status of highly qualified athletes.
Materials and methods. A mathematical and statistical analysis of anonymized medical data on comprehensive medical examination of elite athletes was conducted. Data from 1887 combat sports athletes were processed (n = 1887; males n = 1190; females n = 697). The sample was divided into two groups: athletes without dental pathologies — Group 0 (n = 791; Me median age 21.00 [19.00; 25.00]); athletes with confirmed dental pathologies — Group 1 (n = 1096; Me median age 19.00 [17.00; 24.00]). Diagnoses from endocrinologists and gastroenterologists were also taken into account. Morphometric characteristics and physiological parameters from exercise stress testing were analyzed. Statistical analysis was performed using the StatTech v. 4.6.0 software.
Results. A significant influence of dental diseases on physical performance and endurance was identified. Compared to the group of athletes without a dental diagnosis (Group 0), the presence of a dental diagnosis (Group 1) was associated with statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) across a range of physiological indicators characterizing physical endurance and performance: respiratory exchange ratio R(0) = 1.05 [1.03; 1.09], R(1) = 1.04 [1.03; 1.07]; heart rate at the aerobic threshold level HRAerT(0) = 110.00 [100.00; 122.00], HRAerT(1) = 114.00 [102.00; 126.00]; heart rate at the anaerobic threshold HRAT(0) = 143.00 [132.00; 154.00], HRAT(1) = 147.00 [134.00; 158.00]; peak heart rate at peak load HRpeak(0) = 151.00 [144.00; 160.00], HRpeak(1) = 152.00 [144.00; 163.00]; heart rate at the 3rd min of recovery HR3min(0) = 91.00 [82.00; 101.00], HR3min(1) = 93.00 [84.00; 102.00]; power output at the level of the anaerobic threshold PwrAT(0) = 190.00 [165.00; 230.00], PwrAT(1) = 200.00 [165.00; 240.00].
Conclusions. Dental diseases reduce the performance athletes, in particular at submaximal load levels. This has a negative effect on the training process and competitive results in martial arts. In this regard, a comprehensive prevention program and regular dental checkups are recommended as an essential part of preparation, in particular, in contact sports. The use of individual aligners for mitigating excessive impact on teeth under the conditions of overload and extreme situations is proposed.
AEROSPACE & MARITIME MEDICINE
Introduction. Experimental possibilities during actual spaceflight are limited, making ground-based models, such as dry immersion (DI) and head-down bed rest (HDBR) tests, highly relevant. Changes in bone tissue are induced by alterations in a complex set of environmental factors at the proteomic level, compensating for changes caused by reduced gravity and decreased motor activity. However, upon continued exposure, other regulatory circuits are activated.
Objective. Comparative assessment of proteomic regulation of bone tissue status in 21-day HDBR (tilted at 6°) and 21-day DI tests.
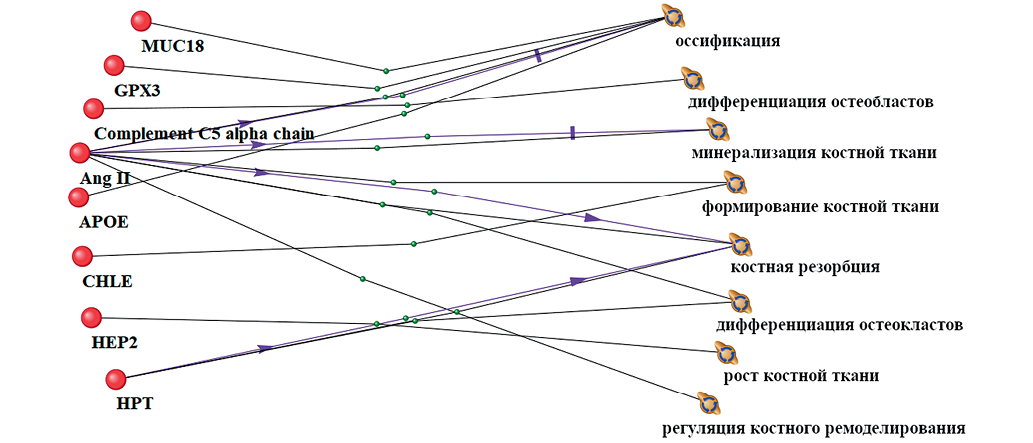
Materials and methods. Using mass spectrometry methods, plasma samples from 8 healthy male volunteer subjects (mean age 20– 44 years) under the conditions of 21-day HDBR and 10 subjects (mean age 23–34 years) under 21-day DI were studied. The Perseus software was used for statistical analysis and identification of molecular functions and biological processes involving the proteins. The correspondence of major biological processes, according to gene ontologies specified in the GO database, and identified proteins was established using the knowledge base of the ANDSystem and STRING.
Results. Nine proteins with significantly altered levels on Day 21 of HDBR (p < 0.05) and eight proteins with significantly altered levels on Day 21 of DI (p < 0.05) were identified. These proteins are associated with biological processes occurring in bone tissue. Some of the identi© Л.Х. Пастушкова, А.Г. Гончарова, Д.Н. Каширина, И.М. Ларина, 2025 fied proteins form stable protein–protein interaction (PPI) networks, indicating potential co-expression. Two common proteins — haptoglobin (Hp) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) — were identified on Day 21 of both DI and HDBR.
Conclusions. The findings offer an insight into the proteomic mechanisms regulating biological processes in bone tissue of healthy individuals under the influence of 21-day HDBR and 21-day DI. Annotations for each protein involved in bone tissue biological processes during 21-day HDBR (tilted at 6°) and 21-day DI are provided. These results are of great importance for aerospace and clinical medicine.
PREVENTIVE MEDICINE
Introduction. The task of maintaining the professional longevity of employees, particularly in technology-intensive and potentially hazardous industries, is becoming increasingly relevant in the context of aging populations and increasing life expectancy. Existing methods for assessing occupational health are in many cases fragmented and fail to account for the entire set of physical, psychological, and social factors. In this article, we address this issue by developing an integral group index of professional longevity (IGIPL).
Objective. The development and implementation of the IGIPL as a tool for quantitative assessment of the level of professional longevity among nuclear industry employees, taking into account morbidity, health status, results of medical examinations and psychophysiological testing, stress levels, and engagement.
Materials and methods. A retrospective study covering the period of 2023–2024 was conducted. The analysis was based on depersonalized data from employees of VNIITF (Snеzhinsk) and the Kalinin NPP (Udomlya). The study included HR reports on morbidity with temporary disability (TD), final reports of periodic medical examinations (PME), annual reports of psychophysiological examinations (PPE), as well as the results of corporate surveys on stress levels (SL) and emotional burnout (EB). We present only relative summary data, without considering working conditions in the index calculation. Standardized methods were used to assess the parameters, including the Perceived Stress Scale-10, the Burnout Assessment Tool, and the E.L. Notkin method for analyzing TD.
Results. The calculation of the IGIPL showed a positive trend. Thus, the index increased by 2.6 points at the Kalinin NPP (a rise from 69.6 to 72.2 points) and decreased at VNIITF (from 67.2 to 65.8 points). The key factor that had the most pronounced negative impact was the high rate of morbidity with temporary disability (1914 days per 100 workers at VNIITF). At the Kalinin NPP, an improvement in the distribution of employees by health groups and a decrease in the proportion of individuals with a high level of emotional burnout were recorded, indicating the effectiveness of the preventive measures implemented by the organization.
Conclusions. The IGIPL has proven its effectiveness as a tool for monitoring professional longevity and identifying risk areas. The study results underscore the necessity for comprehensive programs aimed at reducing morbidity, managing stress, and increasing employee engagement. The IGIPL methodology can be adapted for other industries. Its further elaboration will enhance the accuracy of assessments. The data obtained hold practical significance for developing corporate programs aimed at preserving health and extending the professional longevity of employees.
NEUROBIOLOGY
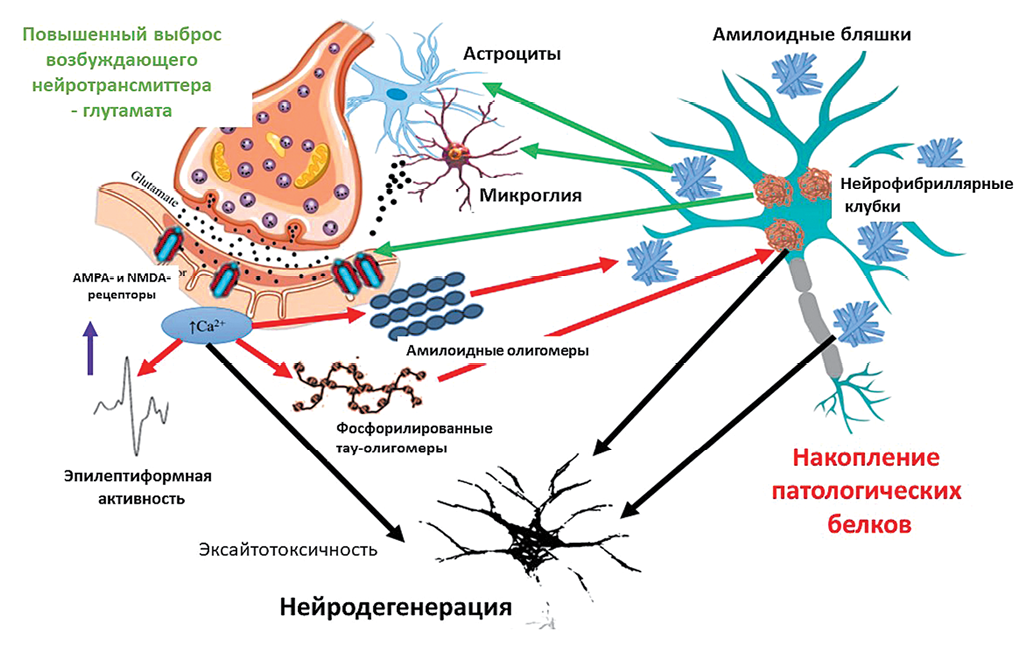
Introduction. The high prevalence and significant disability of patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) necessitate the search for new markers of disease progression and novel treatment approaches. Recent evidence is increasingly attracting the research attention to the value of electroencephalography (EEG) in detecting epileptiform activity in this patient population.
Objective. Detection of the frequency of epileptiform activity in patients with AD and evaluation of its clinical and diagnostic significance.
Discussion. EEG, in particular, prolonged sleep-deprived EEG, is capable of detecting subclinical epileptiform activity, which is associated with more severe cognitive impairments and contributes to disease progression. This review examines research data on the prevalence and clinical significance of subclinical epileptiform activity in AD patients without an epilepsy diagnosis. It also highlights key pathophysiological mechanisms linking epileptiform activity to the progression of cognitive decline in AD. Furthermore, it addresses the rationale for prescribing specific antiepileptic therapy upon detection of subclinical epileptiform activity.
Conclusions. The high clinical significance of performing electroencephalography and detecting epileptiform activity in patients with Alzheimer’s disease, due to its potential negative impact on the progression of cognitive impairments and increased risks of developing epileptic seizures, has been demonstrated.
НEMATOLOGY
Introduction. Severe complications of the novel coronavirus infection (COVID-19) include arterial or venous thromboses, which not only complicate the disease course but also increase mortality. The development of hypercoagulability, which precedes the occurrence of thrombosis, is associated with a significant activation of the hemostasis system, as well as the appearance of microparticles in circulation. These microparticles, generated by activated blood cells, enhance the procoagulant orientation of hemostasis. In this regard, assessment of the prognostic value of changes in hemostasis system parameters associated with the progression and outcome of COVID-19 represents a relevant research task.
Objective. To identify predictors of adverse outcomes of the novel coronavirus infection based on the assessment of parameters characterizing the state of the hemostasis system.
Materials and methods. A total of 163 patients (78 males and 85 females, aged 35–90 years, median age 69 years) were examined during the acute phase of the disease with severe and moderate severity. Depending on the disease outcome, the patients were divided into two groups: the group of survivors (n = 120) and the group of the deceased (n = 43). A study of plasma hemostasis parameters was conducted, including Quick’s prothrombin test, fibrinogen concentration, activated partial thromboplastin time, factor VIII activity, ristocetin cofactor activity, von Willebrand factor content, protein C activity, antithrombin, and free protein S. In addition, the characteristics of microparticles were studied. Statistical processing of the results was performed using the Statistica 12.0 software package.
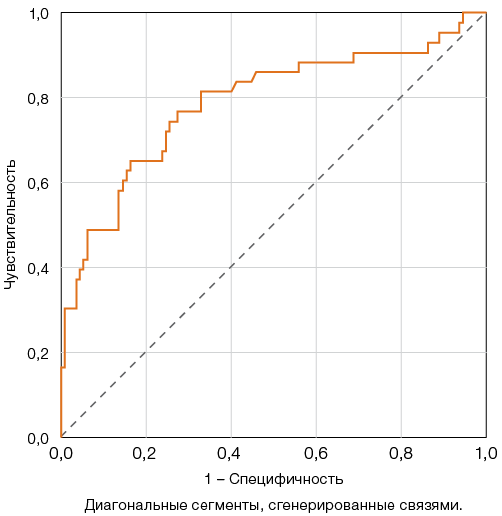
Results. In patients with adverse disease outcomes, a significant decrease in Quick’s prothrombin time (PT) and antithrombin activity was observed, along with an increase in von Willebrand factor activity, D-dimer concentration, and platelet microparticle count. The analysis of sensitivity and specificity of these parameters allowed Quick’s PT less than 70% (sensitivity and specificity were 70% and 74.3%, respectively), D-dimer level more than 800 ng/ml (sensitivity and specificity — 72% and 75.2%, respectively), and platelet MP count more than 3.22% (sensitivity and specificity — 77.8% and 72.7%, respectively) to be considered as threshold values associated with lethal outcome from COVID-19.
Conclusions. Based on the conducted ROC analysis, predictive models for the risk of adverse outcomes of COVID-19 associated with changes in hemostasis system parameters were obtained. The parameters of D-dimer concentration, Quick’s prothrombin time, and platelet microparticle count can be used as laboratory predictors of unfavorable disease progression.
ISSN 2713-2765 (Online)