Introduction. In the context of limited availability of fresh frozen plasma, the use of freeze-dried plasma offers significant logistical advantages in extreme conditions. The effectiveness of freeze-dried plasma depends on the preservation of coagulation potential in the manufacturing process.
Objective. Review of research achievements both in Russia and aboard in the field of freeze-dried plasma technologies, including manufacturing, quality control, and blood component application.
Discussion. Commercial products such as FLyP, LyoPlas N-w, Bioplasma FDP, OctaplasLG Lyo, as well as freeze-dried plasma (Belarus or China), which have proven their effectiveness and safety, are available in glass vials. The production of freeze-dried plasma in polymer containers using membrane technology is a promising direction offering the advantage of using blood components in extreme conditions. The freeze-dried plasma products developed by Terumo BCT Biotechnologies and Teleflex Inc. are currently undergoing clinical trials and are used in military operations to a limited extent. In the Russian Federation, the Lyokon polymer container has been registered. During the lyophilization process, the pH increases to alkaline pH values of 8, which is associated with the removal of carbon dioxide. When assessing the coagulation potential, the most significant decrease is observed in the activity of factor VIII — up to 50%, factor V — up to 37%, protein S — up to 34%, and von Willebrand Factor — up to 25%. The prolongation of prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) is noted. In the Russian Federation, freeze-dried plasma belongs to the group of blood components; therefore, the introduction of foreign production experience (the introduction of cryo- and lyoprotectors, pH adjustment, etc.) is restrained by legislation. This emphasizes the importance of developing domestic technologies.
Conclusions. The production of freeze-dried plasma in polymer containers contributes to uninterrupted transfusion support in the provision of medical care, thus increasing the survival rate of the injured with acute blood loss in emergency situations. In this regard, creation of domestic plasma lyophilization technologies and enhancement of their effectiveness are relevant tasks.
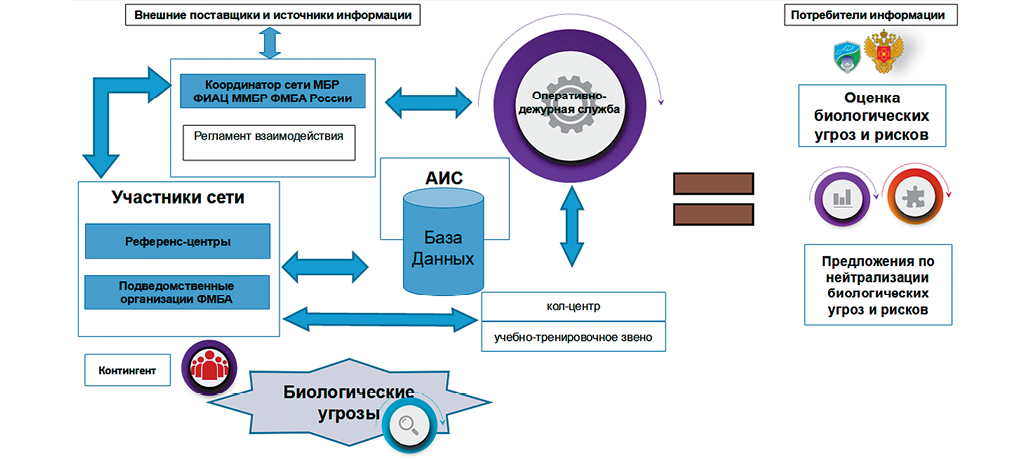
Introduction. The activity aimed at biological risk monitoring (BRM) ensures timely response against emerging biological threats in order to prevent their negative impact on human health. The improvement and further development of the existing network of BRM of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency (FMBA) of Russia requires understanding of its functioning principles.
Objective. Substantiation of the functioning principles of the BRM network in the entitled territories and organizations of the FMBA.
Materials and methods. The study was conducted using the automated information system of the FMBA Center for BRM, which aggregates BRM data from the territories and organizations serviced by FMBA. The methods of systems analysis, reverse engineering, classical logic, analysis, synthesis, comparison, generalization, categorization, and classification were used.
Results and discussion. A comprehensive study of the operating BRM network of FMBA was conducted. Its aims, objectives, functions, characteristics, and activities were examined. Using the method of reverse engineering, 19 key principles of the BRM network were substantiated. These principles were classified based on stratification of classes according to the types of activities that ensure the BRM network functioning as a complex organizational system. As a result, the principles were distinguished into informational and technological, organizational and managerial, and scientific and practical classes.
Conclusions. The functioning principles of the MBR network in the territories and organizations serviced by the FMBA were identified, formulated, substantiated, and classified. These include the use of the systems approach, the principle of continuous monitoring and reporting, the principle of comprehensive information and analytical support, etc. The results obtained can be used as the basis for decision making when optimizing the technology of BRM monitoring by FMBA.
Introduction. Prior to use in the production of food additives, ingredients, and biologically active substances, wild plants should be assessed in terms of heavy metal (HM) accumulation. This task is also relevant because wild plants can be consumed by the survived after accidents, disasters, or military operations at sea.
Objective. To assess the HM-related danger of coastal flora in the areas of potential landing of shipwrecked crews in the seas of the Russian Federation.
Materials and methods. The study objects were coastal algae and higher plants growing in the coastal area of the Gulf of Finland. Plant samples were collected in the Bolshoy Beryozovy Island, Hogland Island, and the Kurgalsky Peninsula. Prior to elemental analysis, the samples were dried at 80°C to a constant weight; their dry weight was estimated with an accuracy of 1 mg. The raw mass was estimated based on the dry weight data and the assumption that the water content in native tree leaves comprises 75%, in grass leaves — 85%, and in F. vesiculosus thalli — 70%. The dried material was mineralized by an MS-6 microwave sample preparation system (Volta, Russia). Elemental analysis was performed using an MGA-915M atomic absorption spectrometer. The measurement results were processed using the Statistica software.
Results. The Cu and Pb content in the studied plants was found to range within permissible limits. The permissible level of cadmium was exceeded by 2–4 times in A. ptarmica, C. angustifolium, and U. dioica on the Kurgalsky Peninsula, indicating the risk of food consumption. The minimum values of Mn content (less than 20 mg/kg of dry matter) were typical of two plant species (L. japonicus and Salix sp.) from the Bolshoy Beryozovy Island and A. podagraria from the Kurgalsky Peninsula. The toxic effects of Mn begin to appear when the daily intake exceeds 2 mg/day, while the maximum Mn content in the studied objects was 11.9 mg/kg. The high Zn content was typical of all plants on the Hogland Island, as well as T. repens and A. podagraria from the Kurgalsky Peninsula and Salix sp. and L. japonicas from the Bolshoy Beryozovy Island. The maximum amount of plant material that can be safely consumed was calculated to be approximately 0.17 kg/day of raw leaf mass.
Conclusions. The absence of daily intake limits for essential elements in regulatory documents makes it difficult to assess the severity of consequences of using plant raw materials for food and medicinal purposes and to apply a risk-based approach to assessing food safety. The high degree of danger associated with the use of plants from the Kurgalsky Peninsula (A. ptarmica, C. angustifolium, and U. dioica) is due to a significant excess of Cd limits. The Cu and Pb levels in all the studied plants was below the limits, indicating the absence of danger associated with these elements. The Zn content can be considered safe, since more than 1 kg of raw leaf mass must be consumed daily to meet the daily requirement, which is practically impossible in actual conditions.
Introduction. Abdominal gunshot wounds account for 4.7–16.2% of injuries among their total number. Such wounds carry a high risk of fatal outcomes (depending on the nature of the wound, whether isolated or combined), as well as a large number of complications. In this regard, provision of proper and timely pre-hospital medical care is a highly important task.
Objective. To assess the extent and quality of pre-hospital medical care provided to civilians with gunshot abdominal wounds.
Materials and methods. The quality of emergency medical care was assessed based on a retrospective analysis of source documents: run sheets (Form 114/u), and records of 60 civilian patients (47 (78.3%) men and 13 (21.7%) women; average age 35 ± 5 years) in the special military operation (SMO) war zones. All injured were divided into two groups: (1) 46 (76.7%) wounded patients having received medical care from emergency medical teams (EMT) staffed with physicians and (2) 14 (23.3%) wounded patients having received medical care from EMTs staffed with paramedics. The EMT response time and extent of medical aid were assessed. The severity of the patient’s state was assessed using the Battlefield Surgery Emergency Scale.
Results. It was found that the ambulance response time varied 5–30 min and averaged 24 ± 4 min for physician EMTs and 21 ± 6 min for paramedic EMTs, which can generally be described as normal. In total, 57 (85%) wounded had projectile wounds, with gunshot wounds being recorded in 3 (5%) cases. Multiple wounds were predominant in 52 (86.7%) cases, whereas single wounds were noted in 8 (13.3%) cases. A non-severe, severe, extremely severe, and critical state was recorded in 38 (63.3), 9 (15%), 12 (15%), and 1 (1.7%) patients. In the vast majority of cases (54 (90%)), the provided care was timely, proper, and to the full extent. At the same time, in 6 (10%) cases, the extent of provided emergency medical care could be considered insufficient: in 2 (3.3%) cases with physician EMTs and in 4 (6.7%) with paramedic EMTs. The errors were related to underestimating the severity of the patient’ state, which resulted in inadequate anesthesia and infusion therapy, i.e., the absence of antishock actions.
Conclusion. Pre-hospital medical care to injured civilians with abdominal gunshot wounds is provided by physician and paramedic EMTs. The extent of medical aid includes wound treatment and aseptic dressing application, adequate anesthesia, and antishock actions. A lower error rate in the provision of emergency medical care by physician EMTs in comparison with paramedic EMTs was observed. Centralized measures should be implemented to improve both the theoretical knowledge and practical skills of EMTs in providing pre-hospital emergency medical care for abdominal gunshot wounds. To that end, it is necessary to involve surgeons and disaster medicine specialists in training emergency medical personnel.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Introduction. Anticancer inhibitors of plant and fungal origin (IPFOs) represent a promising direction in antitumor therapy, offering a variety of mechanisms of action, in most cases different from conventional chemotherapeutic drugs. As a rule, IPFOs simultaneously affect several metabolic pathways, exerting a combined effect on different targets in the cancer cell and reducing the risk of drug resistance development.
Objective. To study promising directions in the development of new antitumor drugs, to generalize current data on the IPFO mechanism of action in the context of a combined approach to cancer treatment.
Discussion. Compounds exhibiting antitumor activity are increasingly attracting the research attention. Due to their diverse mechanisms of action, anticancer IPFOs represent a promising direction in cancer treatment. A large number of conventional chemotherapy drugs, although being of plant origin, demonstrate high effectiveness, which confirms the relevance of searching for new anticancer IPFO compounds. Solid tumors exhibit a pronounced ability to both proliferate and induce angiogenesis, which justifies the current active search for new plant-derived compounds with antiangiogenic properties, along with other IPFOs. As a rule, anticancer IPFOs simultaneously affect several metabolic pathways, exerting a combined effect on different targets in the cancer cell and reducing the risk of drug resistance.
Conclusions. This review has examined the molecular mechanisms of IPFO action, including suppression of angiogenesis and cancer cells proliferation, apoptosis induction, cell cycle modulation, and direct cytotoxic effect by stimulating the activity of CD8+ T lymphocytes, NK cells, and macrophages.
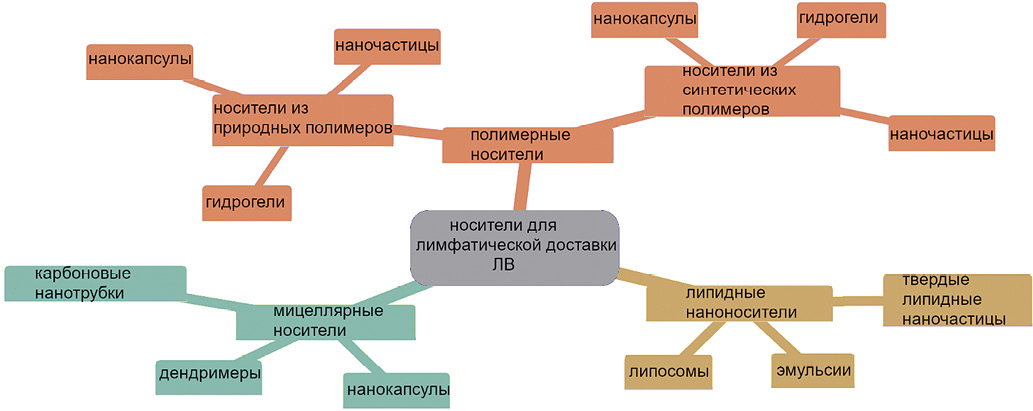
Introduction. The targeted delivery of lipophilic chemotherapeutic and immunomodulatory agents through the lymphatic system is a promising approach in cancer treatment. Lipid-based carriers (e.g., liposomes) are able to not only to enhance the solubility and stability of drugs, but also to ensure their protection from degradation in the gastrointestinal tract. Research into the potential of lymphatic delivery of bioactive substances using liposomes can further improve the effectiveness of lipophilic drugs.
Objective. To study the prospects for using first-generation soy lecithin-based liposomes (cholesterol-free) as a lymphatic carrier for biologically active substances.
Materials and methods. Liposomes were prepared from soy lecithin containing green fluorescent protein GFP (with a maximum fluorescence at a wavelength of 506 nm) using the method of thin-film hydration/rehydration. Some liposomes were modified by 1%, 0.5%, and 0.1% chitosan solutions. The GFP incorporation into the liposomes was visualized using confocal microscopy. In vivo studies were conducted in three groups of female Balb/c mice aged 11–13 weeks (three animals in each): a control group; a group receiving native fluorescent protein, and a group with the design formulation (liposomes containing fluorescent protein). After intake, the small intestine was retrieved followed by its preparation and cryosection staining. The analysis of the cell suspension was performed using a CytoFLEX V5-B5-R3 flow cytometer.
Results. The confocal microscopy study found the particle size of the liposomes obtained by the thin-film hydration method to range within 1–5 μm. The incorporation of the model protein into the liposomes, as evidenced by its content before and after the liposome formation, was at least 60%. In vivo experiments on mice found that intragastric administration of fluorescent protein-containing liposomes enables successful protein delivery to the intestinal wall.
Conclusions. Soy lecithin-based liposomes were obtained using the thin-film hydration method. Confocal microscopy was used to evaluate the size of the obtained liposomes and to assess qualitatively the incorporation of green fluorescent protein. The incorporation of chitosan into the liposome shell resulted in a significant aggregation of the final product, which may reduce the effectiveness of liposome delivery to cells. Confocal microscopy of cryosections and cytofluorometry of cell suspensions obtained from small intestine fragments showed the capacity of the engineered system to deliver fluorescent protein and, possibly, intact liposomes to the intestinal wall.
GENETICS
Introduction. Due to the active development of multiomics technologies, more and more information about human genetic and immunological research is becoming available. Data repositories are used to systematize and store such information, which facilitates the search and use of information for carrying out scientific research and solving applied problems in the area of medicine.
Objective. To analyze the global experience of using repositories of human genetic and immunological data to define their functional features and role in the development of population immunology and genetics.
Discussion. Functional features of genetic and immunological data repositories were analyzed. The data on the repositories included in the study was obtained from open sources. The selection process for repositories included three stages: selection of scientific publications, deduplication, and filtering based on selection criteria. The main criteria for the subsequent evaluation of human genetic and immunological data repositories were as follows: data volume, data accessibility, and data formats. The search for information about repositories and biobanks in the Russian Federation was conducted using online search queries on the Internet. The study analyzed 15 largest genetic and immunological data repositories, of which 37.5% are affiliated with the UK and 43.75% are affiliated with the USA. The task of creating and maintaining large repositories is solved, as a rule, by forming international and inter-institutional consortia. The availability of genetic data repositories is ensured by a combination of technological, organizational, and legal mechanisms. The most common sources of repository funding are state budgets, funds from private foundations and charitable organizations, and investments from pharmaceutical companies. The main risks associated with the operation of a repository can be divided into four groups: ethical, legal, biological, and technological risks related to data privacy. In the Russian Federation, genetic research is one of the most rapidly developing scientific directions. As a result, the challenges of secure storage, ethical use, and legal protection of data are acquiring particular importance. The presented review discusses possible directions for further development of national genetic and immunological data repositories, as well as the possibilities of additional regulation of genetic data handling at the legislative level.
Conclusions. The conducted review has identified possible risks associated with repository functioning and proposed various approaches to minimizing these risks and optimizing the development of data repositories. One of the most promising areas is the development of AI-based integration modules for processing and annotating data presented in standardized protocols.
Introduction. The development of symptoms in post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is determined by a set of factors, which are not limited to classical neurotransmitter systems in the brain or stress hormones. In particular, the brain renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system may be involved in the mechanisms of PTSD.
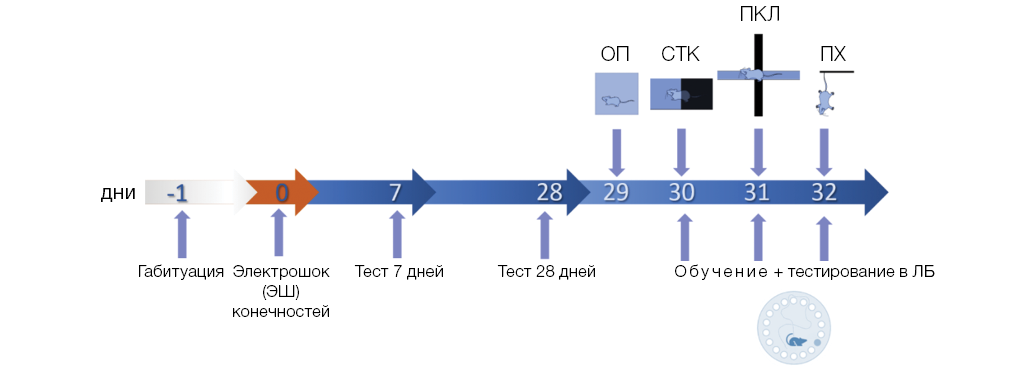
Objective. To study the effect of hACE2 expression, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) gene, on anxiety and susceptibility to psycho-physiological stress in mice in the foot electroshock (FS) model of PTSD.
Materials and methods. The experiments were conducted using 4–5-month-old male C57Bl/6N and k18-hACE2-KI mice. C57Bl/6N mice were divided into three groups: control (n = 7); the foot shock (FS) (n = 7); FS + lisinopril (n = 7). k18-hACE2-KI mice were divided into two groups: control (n = 7) and the FS (n = 8). Pavlovian fear conditioning was performed using FS as an unconditioned stimulus. Mice in the FS + lisinopril group received lisinopril at a dose of 10 mg/kg per day with drinking water for 28 days after psychophysiological trauma. The expression of fear, reflecting the memory of psychophysiological trauma, was assessed on day 7 and day 28 after FS exposure. The magnitude of the fear response was assessed by evaluation of the relative time of freezing. The open field test was used to assess general locomotor activity. The tail suspension test was used to assess the stress-coping strategy, while the light-dark box test and the elevated plus maze test were used to measure anxiety. The Barnes maze test was used to explore spatial navigation and spatial learning dynamics. Behavior was analyzed using the ANY-maze Video-Tracking Software. Statistical analysis was performed using the Prism GraphPad v.10.0 software.
Results. k18-hACE2-KI mice with expression of humanized ACE2 gene under the control of the cytokeratin gene promoter showed a more pronounced ability to remember and retain the memory about the conditioned stimulus/context of the traumatic event in the PTSD-model when compared to C57Bl/6N mice. Anxiety measured in the light-dark box test was lower in k18-hACE2 mice than C57Bl/6N mice after FS. At the same time, there was a decrease in the open-field motor activity and there were no changes in spatial memory in the Barnes maze test. Lisinopril, an ACE inhibitor (28 days after FS), did not reduce traumatic memory in C57Bl/6N mice, indicating that the promnestic effect of hACE2 gene expression is not a result of systemic hypotension and pointing at the involvement of the central mechanisms in the realization of hACE2 gene effect in the pathological phenotype development.
Conclusions. The data indicate that the hACE2 gene affects the stress response in mice. Specifically, the expression of hACE2 gene in mice leads to increased memory of psychophysiological trauma and reduced extinction of traumatic memory compared to wild-type mice. This may be due to the modulation of the ACE2-dependent renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in the brain. The decreased RAAS activity under the action of the ACE inhibitor lisinopril with a hypotensive effect did not affect memory in wild-type mice.
MICROBIOLOGY
Introduction. Low-temperature argon plasma (LTAP) has been widely studied as an alternative approach to prevention of purulent infections in cases of reduced germicide effectiveness due to the developed pathogen resistance.
Objective. Survival assessment of opportunistic pathogens under the action of LTAP exposure in in vitro models.
Materials and methods. The study was carried out using ESKAPE clinical strains (a “superbug” group with a high epidemic potential for the formation of hospital strains) and reference strains from culture collections, as well as strain mixtures. A PLASMORAN plasma arc unit (Russia) was used as a LTAP source. One plasma generation mode, three distance variants (from the nozzle to the Petri dish culture plane — 10, 15, and 20 cm), four LTAP exposure options (15, 30, 45 s for bacteria and 30, 45, and 60 s for fungi) were used. Pathogens survival after LTAP exposure in vitro was assessed by bacterial growth inhibition.
Results. LTAP showed a significant antimicrobial action against clinical strains of ESKAPE Gram-negative bacteria K. pneumoniae, R. aeruginosa, A. baumanii, E. coli, Gram-positive bacteria MRSA and yeast-like fungi C. albicans under an exposure duration of 30–45 s for bacteria (the required dose of UV-A radiation is 37.8 J/m 2 UV-B 15.9 J/m2 UV-C 34.2 J/m2) and a distance of 10–15 cm from the plasma generator nozzle. The antimicrobial effect is manifested in the absence of pathogen growth on culture media at the site of LTAP exposure at a certain exposure dose, duration, and distance. This effect ensures a decrease in the titer of viable microorganisms not only in monocultures, but also in bacterial associations, both in reference strains from culture collections and in ESKAPE clinical strains.
Conclusions. PLASMORAN-generated LTAP exhibits significant antibacterial and antifungal effects with respect to both reference strains from culture collections and ESKAPE clinical strains. The efficacy of LTAP action ensures a decrease in the titer of viable microorganisms from 10 8 –10 9 CFU to single CFU. The greatest effect of LTAP conditions (UV-A radiation dose of 37.8 J/m2; UV-B 15.9 J/m2; UV-C 34.2 J/m2) on bacterial cultures is observed under a distance of 10–15 cm and an exposure duration of 30–45 s. The optimal conditions for fungi (UV-A radiation dose of 168.6 J/m2; UV-B 68.4 J/m2; UV-C 159 J/m2) are a distance of 10 cm and an exposure duration of 60 s. Under standard dose, exposure duration, and distance, A. baumannii and E. faecium are more resistant to LTAP action than other studied bacteria. C. albicans is more resistant to LTAP action compared to bacteria, requiring a longer exposure and a shorter distance from the plasma generator nozzle to the treated surface. The results obtained require further study.
AEROSPACE & MARITIME MEDICINE
Introduction. In the stratosphere, when the aircraft cockpit is depressurized, the pilot switches to breathing pressurized oxygen. However, breathing under such conditions leads to the development of adverse processes that affect the functional state of the body and reduce the quality of aircraft piloting. Programs of psychophysiological training of pilots for such conditions include breathing and speech training under oxygen overpressure.
Objective. Effectiveness assessment of a five-day breathing and speech training course under oxygen overpressure in Vietnamese test subjects.
Materials and methods. The study involved 35 Vietnamese test subjects aged 19–32. The assessment of the development of breathing skills under oxygen overpressure (OOP) was based on the dynamics of psychological parameters and the pronunciation accuracy of control words. The study used a KM-35 demand oxygen mask in combination with a ZSh-7A pilot protective helmet and a VKK-15 altitude compensating suit to create counterpressure on the chest. OOP was created using the BARS-GD hardware and software complex. The developed course of breathing and speech training under OOP consists of five OOP breathing sessions, which are conducted once a day during five consecutive days. Each session involves breathing under OOP in a sequential and continuous manner at five stages with a breathing time of 2 min at each stage. OOP was created at levels ranging 150–1000 mmHg. The functioning of the central nervous system (CNS) was assessed based on the average time of simple and complex visual-motor reactions (SVMR, CVMR) and the response to a moving object (RMO). The level of situational anxiety, well-being, activity, and mood was assessed using the wellbeing, activity, mood (WAM) questionnaire. Statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS 26 software.
Results. As a result of the five-day training course, a statistically significant decrease in the pre-stress level of situational anxiety by 3.9% was observed. Prior to the training course, in the setting of simulated rapid cockpit decompression, a decrease in well-being and mood indicators by 3.7% and 5.7%, respectively, was noted. In addition, the experiment recorded an increase in psychophysiological reserves, which was confirmed by statistically significant changes in the time of simple and complex visual-motor reactions, as well as the results of testing the response to a moving object before and after the training course.
Conclusions. The data obtained confirmed the effectiveness of the developed five-day training course, as a result of which the test subjects increased their psychological and psychophysiological readiness to perform tasks under conditions of a sharp decrease in pressure in the pressurized cabin of an aircraft and the operation of high-altitude equipment. The developed five-day training regime of Vietnamese military personnel is recommended for integration into the training system of pilots for high-altitude and stratospheric flights.
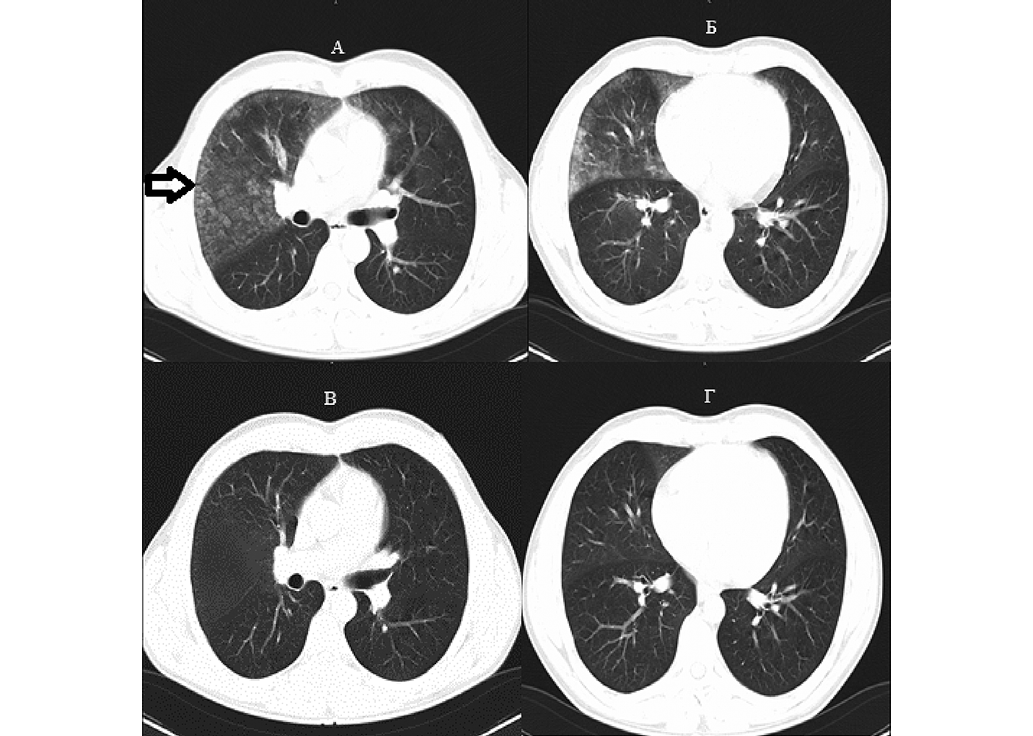
Introduction. Immersion pulmonary edema (IPE) is a pathological condition that occurs in an aquatic environment during various activities, such as underwater engineering, scuba diving, triathlon competitions, etc. Despite a significant number of English-language publications, the problem of IPE remains insufficiently studied in Russia.
Objective. Research into the diagnosis, clinical manifestations, treatment, and prevention of IPE to optimize medical care for this pathological condition.
Discussion. The main factors leading to IPE include exposure to cold water, intense physical exertion during swimming, increased blood pressure while in water, excessive fluid intake before swimming, age over 50. Breathing 100% oxygen underwater can cause hyperoxia, oxidative stress, disruption of the alveolar–capillary membrane integrity, and surfactant deficiency, leading to fluid transudation into the pulmonary interstitial tissue and edema. Hyperoxia induces pulmonary vasoconstriction, increases hydrostatic pressure, and enhances fluid filtration into the interstitium, exacerbating IPE and contributing to the development of alveolar pulmonary edema. Clinically, IPE presents with labored breathing, acute dyspnea, coughing with hemoptysis, frothy bloody discharge, and other symptoms. A distinctive feature of this condition is the resolution of key symptoms within 48 h. On physical examination, percussion over the affected lung area reveals dullness, while auscultation detects wet rales in the lungs and murmurs characteristic of acute mitral regurgitation with left ventricular failure. Computed tomography findings include ground-glass opacities, peribronchial infiltration, and pleural effusion, predominantly on the affected side. A major limitation of this method is the inability to perform imaging immediately during an emergency ascent. Ultrasound diagnostic markers of IPE include hyperechoic reverberation artifacts (B-lines), produced by the interaction of ultrasound waves with air-fluid content in the alveoli, typical of pulmonary edema. Clinical and laboratory markers of IPE include elevated levels of copeptin, brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), ischemia-modified albumin, and high-sensitivity troponin T.
Conclusions. IPE remains an understudied yet highly dangerous pathological condition in diving and aquatic swimming. Therefore, it is crucial to educate divers, combat swimmers, professional scuba divers, and athletes (triathletes, swimmers) about preventive measures and symptom recognition when they occur during surface or underwater activities. Implementing a comprehensive approach to IPE prevention will reduce the incidence of this condition and enhance the safety of diving operations.
SPORTS MEDICINE
Introduction. When assessing bone metabolism markers in athletes under the age of 18, it should be borne in mind that, in comparison with adults, the pediatric population is characterized by higher values of these markers. Their maximum increase during puberty coincides with peak bone mass gain.
Objective. To evaluate bone metabolism status in healthy high-performance athletes under the age of 18 based on the levels of C-terminal telopeptide (β-CrossLaps), osteocalcin, and N-terminal propeptide human procollagen type 1 (P1NP) in the blood serum.
Materials and methods. A single-center, сross-sectional study involved 383 juvenile athletes aged 13–18 years (248 girls and 135 boys; average age 15.2 [14.0; 16.1] years) from Russian national sports teams. The study was conducted in the period from March 2021 to July 2023. All athletes were divided into groups according to age and gender. The male groups were as follows: 13.1–14.0 years old (n = 3); 14.1–15.0 years old (n = 11); 15.1–16.0 years old (n = 43); 16.1–17.0 years old (n = 42); and 17.1–18.0 years old (n = 36). The female groups were as follows: 13.1–14.0 years old (n = 17); 14.1–15.0 years old (n = 51); 15.1–16.0 years old (n = 65); 16.1–17.0 years old (n = 59); and 17.1–18.0 years old (n = 56). The serum levels of osteocalcin, C-terminal telopeptide, and procollagen type 1 were evaluated in all athletes. The sexual maturity rating (SMR) was assessed according to the Tanner Scale. Statistical data processing was performed using the Statistica 10.0 software package (StatSoft Inc.; USA).
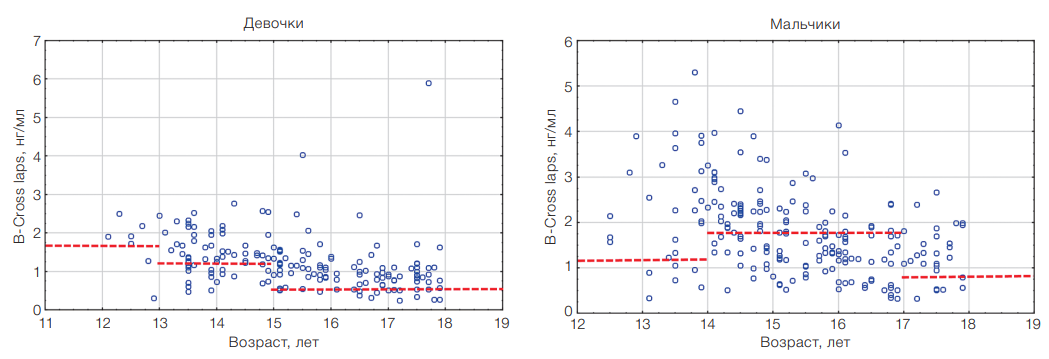
Results. The maximum values of β-CrossLaps in boys (2.27 [1.14; 3.45] ng/mL) and girls (1.55 [1.10; 2.02] ng/mL) were observed at the age of 13–14 years. The levels of osteocalcin and P1NP in young high-performance athletes corresponded to the standards for children with a normal level of physical activity. The maximum values of P1NP were revealed at the age of 13–14 years in both male (767.8 [148.1; 1142.4] ng/ mL) and female (450.5 [268.6; 569.3] ng/mL) groups. In boys, the maximum values of osteocalcin (125 [89; 144] ng/mL) were detected at the age of 14–15 years; in girls (86 [62; 131] ng/mL) — at the age of 13–14 years.
Conclusions. In young high-performance athletes, the β-CrossLaps level as the main marker of bone resorption significantly exceeds the population norms for children and adolescents with a normal level of physical activity. When assessing the level of β-CrossLaps, osteocalcin, and P1NP, reference values should be adjusted to account for the gender and sexual maturity stage of athletes. The data obtained can be used when interpreting the results of an in-depth medical examination of athletes from Russian national sports teams to identify bone remodeling disorders.
Introduction. Predictive modeling in healthcare is a rapidly evolving field of scientific knowledge at the intersection of information technology and medicine. In sports medicine, the importance of accurate forecasting of physical performance parameters in response to changing environmental conditions cannot be overstated. For athletes, such information provides a crucial competitive advantage before major competitions.
Objective. Development of methods and approaches to analyze clinical data obtained through comprehensive medical examinations of athletes.
Materials and methods. An analysis of anonymized medical data from comprehensive medical examinations was conducted for 6222 world-class athletes (3792 males and 2430 females) with a mean age of 23.3 ± 5.1 years. The data were stratified by sex and according to sports categories: cyclic sports (1376 athletes, including 861 males and 515 females); complex coordination sports (1342 athletes, including 761 males and 581 females); team sports (1618 athletes, including 980 males and 638 females); and combat sports (1886 athletes, including 1190 males and 696 females). The analysis included both clinical data on the presence (or absence) of pathological conditions identified during specialist medical examinations and physiological parameters from bicycle ergometer stress testing. Statistical analysis was performed using the Stat-Tech v. 4.6.0 software (StatTech, Russia).
Results. Using regression analysis, statistically significant (p < 0.001) predictive models for a set of physical performance parameters were developed, which revealed over 40 associations with clinical diagnoses made by medical specialists. The strongest correlations were observed between physical performance indicators and dental diagnoses. Future research will focus on creating a mathematical model to predict performance decline in world-class athletes, based on an analysis of disease development risk factors.
Conclusions. The developed and implemented approaches for analyzing clinical data from comprehensive medical examinations of world-class athletes enabled the creation of effective predictive mathematical models of physical performance parameters using linear regression methodology, while accounting for the presence/absence of identified diagnoses. The proposed models provide a comprehensive assessment of athletes’ functional status, thus allowing accurate prediction of physical performance levels and optimization of professional training by minimizing risks of overtraining and sports-related injuries.
CLINICAL LABORATORY DIAGNOSTICS
Introduction. The worsening problem of drug abuse in Russia and the growing number of hidden users of narcotic drugs (ND) require the list of screening examinations for ND identification to be extended by including more economical approaches that reduce costs at the stages of collection, transportation, storage, and analytical examination of biological samples.
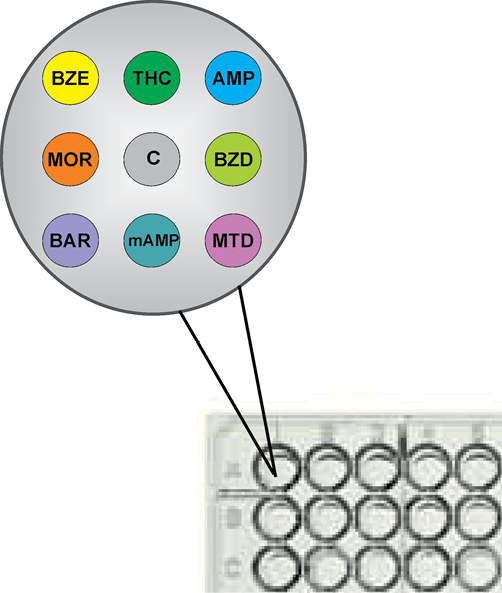
Objective. Development of a multiplex immunoassay method based on the PHOSPHAN technology for detecting the main groups of narcotic and psychotropic substances in pools of paper-dried urine samples, followed by an assessment of its potential for identifying drug addicts as part of an extended drug control program.
Materials and methods. Dry urine samples (n = 31) were prepared on paper test strips from liquid samples containing (n = 30) or non-containing (n = 1) cocaine, cannabinoids, amphetamines, opiates, benzodiazepines, barbiturates, methamphetamine, or methadone, according to toxicology screening (TS). The samples were studied as pools containing 1–40 fragments (0.45×0.45 cm) of test strips. The luminescent signal was recorded on a microplate immunochip using an IFI-05 photoluminescence pulsed indicator. The ND presence in the samples was assessed by the inhibition rate of antibody binding in the related microplate test zone (B/B0 ratio). Statistical processing of the results was carried out using the standard Microsoft Office package.
Results. The inclusion of dry urine samples in the pools (up to 10), where only one contained the target ND, had no significant effect on the capability of the method to detect NDs with sensitivity levels that meet the TS requirements. The following substances were detected: cocaine (2 samples), cannabinoids (11 samples), amphetamines (6 samples), opiates (9 samples), benzodiazepines (7 samples), barbiturates (10 samples), methamphetamine (7 samples), and methadone (6 samples), including samples with high concentrations of opiates and amphetamines.
Conclusions. A method of multiplex phosphorescence microplate immunoassay has been developed for the detection of eight main groups of NDs and psychotropic substances in pools of paper-dried urine samples (dried urine spot, DUS). The detection limits of the studied NDs in extracts from DUS test-strips were 2–8 ng/mL, which is significantly lower than the detection limits recommended for screening examination. The proposed approach can form the basis of a new screening methodology that includes collection of urine samples, their application onto filter paper test-strips, and transportation to a laboratory for the examination of individuals at industrial facilities of critical importance. The use of the developed multiplex phosphorescence immunoassay and pooled urine samples will significantly reduce the test cost (by more 10-fold) compared to conventional immunochromatographic assays.
CLINICAL MEDICINE
Introduction. Primary immunodeficiency disorders (PID) are a group of congenital diseases caused by genetic defects that lead to diverse phenotypic manifestations. Classic inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) are typically multifactorial pathologies, combining genetic predisposition, gut microbiota alterations, and adverse environmental influences. Very early-onset IBD (VEO-IBD), defined as a disease presenting before six years of age, accounts for 3–15% of all pediatric IBD. This subgroup is particularly characterized by monogenic etiology, associated with gastrointestinal phenotype PID and with causative mutations in specific genes.
Case report. We present a clinical case of monogenic Crohn’s disease in a child with X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome type 2 (XLP-2), treated using a multi-stage team approach. To achieve sustained remission, in addition to selecting conservative therapy, repeated surgical interventions and repeated hematopoietic stem cell transplantations were required. An individualized approach and treatment strategy planning enabled a positive treatment outcome.
Conclusions. In young children with the presence of atypical IBD and refractoriness to standard therapy, it is crucial to differentiate monogenic forms of IBD. Such patients require close monitoring, dynamic follow-up, and a multidisciplinary approach involving collaboration between gastroenterologists, immunologists, and surgeons.
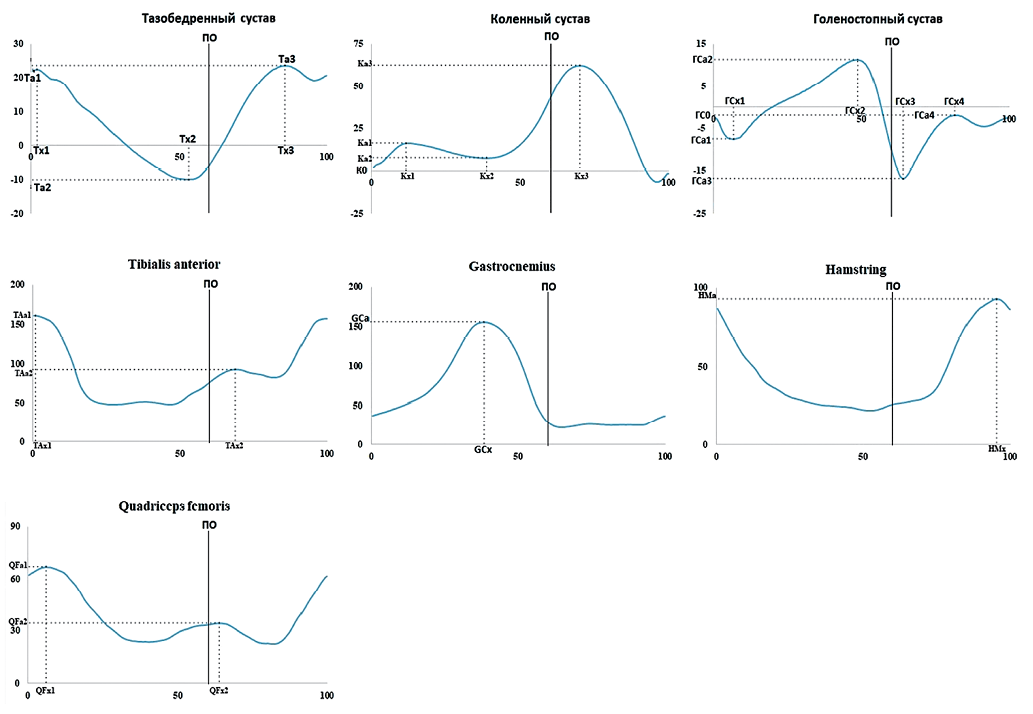
Introduction. Gait dysfunction is a complication of acute cerebrovascular accidents, which is biomechanically manifested as reduced speed and asymmetry in spatiotemporal and kinematic parameters. These impairments can be corrected using functional electrical stimulation (FES) of muscle contraction; however, the available literature primarily describes its application during the late recovery phase of stroke.
Objective. Evaluation of the potential of multichannel FES for gait recovery in early post-stroke rehabilitation.
Materials and methods. The study included 11 patients (2 females and 9 males) aged 46–66 years in the early recovery period after an ischemic stroke (time since stroke onset was 69.1 ± 52.0 days) and 34 healthy subjects (18 females and 16 males) as a control group. The lower limb muscle strength and tone were assessed using the Medical Research Council Scale for Muscle Strength and the modified Ashworth scale, respectively. Gait function was evaluated using the Dynamic Gait Index, Hauser Ambulation Index, Timed-Up-and-Go test, and 10-Meter Walk test. Gait pattern function (b770), obstacle negotiation (d4551), and short-distance walking (d4500) were also examined. All patients underwent a FES therapy course (mean number of sessions — 10.8). Clinical and biomechanical examinations were performed before and after the FES therapy course. Biomechanical gait analysis was conducted using a Stadis system (Neurosoft, Russia). Statistical analysis was performed using the Statistica 12.0 software.
Results. The conducted clinical evaluation demonstrated a minor yet statistically significant functional improvement in post-treatment testing. An increase in the scores of Dynamic Gait Index and 10-Meter Walk test was observed. A decrease in the values of Hauser Index values and the completion time of Timed- Up-and-Go test, as well as in domains (d770) and (d4500), was noted. Gait function showed improvement. The values of walking speed (p < 0.05), double support time on the paretic side (p < 0.05), and m. gastrocnemius activity on both the paretic and unaffected sides (p < 0.05) increased.
Conclusions. The observed changes in gait function were typical of hemiparesis. During the FES therapy course, the patients showed no negative reactions. The clinical and biomechanical gait functions of patients showed minor but positive changes during the FES therapy course. Among biomechanical parameters, the amplitude of the gastrocnemius muscle course on the paretic side significantly increased, which is one of the FES target parameters. Short courses of multichannel FES can be applied in this patient category; however, their effectiveness is insufficient. Approaches to improving the FES effectiveness require further investigation.
PUBLIC HEALTH
Introduction. Due to the current decline in medical professionals’ interest in the institution of qualification categories, the problem of improving the quality of information content and its distribution among the target audience becomes particularly relevant.
Objective. Quality assessment of the website informativity of territorial attestation commissions and public health administrations of the Russian Federation (RF) subjects regarding the assignment of qualification categories.
Materials and methods. The information search about the procedure for attesting healthcare specialists was carried out through 47 websites of the healthcare executive authorities of 83 RF subjects and territorial attestation commissions. A remote survey of 47 medical professionals was conducted: 25 (53.2%) men and 22 (46.8%) women (the average age of respondents was 32.3 ± 4.94 years) with a work experience in the specialty of two years. Each respondent reviewed the information about the attestation procedure posted on the websites of three different RF subjects. The websites were distributed among respondents randomly using an online random number generator. The survey was conducted using a questionnaire developed by the Department of Economics and Marketing at the Academy of Postgraduate Education of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia. Statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS software (IBM Company).
Results. In total, 47 (56.6%) websites of territorial attestation commissions contained information on all points of the Order of Ministry of Public Health of the Russian Federation (No. 458n dated August 31, 2023), regarding the rules and procedure for submitting documents. In the survey, the information sufficiency on the rules and procedure for attestation of medical professionals was rated higher (3.13 ± 1.04 points) compared to the information clarity (2.98 ± 1.02 points) (p = 0.009). The respondents’ scores of the sufficiency and clarity of information on different websites differed significantly: 102.155 ≤ χ2 ≤ 110.978 (p ≤ 0.001); for the same websites, the scores were identical (p = 0.881 and p = 0.976).The scores of information sufficiency and clarity did not depend on the respondents’ age (p = 0.416 and p = 0.706), gender (p = 0.163 and p = 0.148), or profession (p = 0.901 and p = 0.947), or their work in organizations that provide care in different settings (p = 0.956 and p = 0.983).
Conclusions. The information about the attestation procedure of medical professionals, which is available on the websites of the public health authorities of RF subjects and on the websites of the respective territorial attestation commissions, needs to be corrected and updated.
ISSN 2713-2765 (Online)